Donation after circulatory death heart transplantation using normothermic regional perfusion:The NYU Protocol
- PMID: 36820336
- PMCID: PMC9938390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjtc.2022.11.014
Donation after circulatory death heart transplantation using normothermic regional perfusion:The NYU Protocol
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of cardiopulmonary bypass for thoraco-abdominal normothermic regional perfusion on the metabolic milieu of donation after cardiac death organ donors before transplantation.
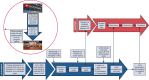
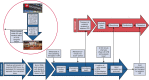
Methods: Local donation after cardiac death donor offers are assessed for suitability and willingness to participate. Withdrawal of life-sustaining therapy is performed in the operating room. After declaration of circulatory death and a 5-minute observation period, the cardiac team performs a median sternotomy, ligation of the aortic arch vessels, and initiation of thoraco-abdominal normothermic regional perfusion via central cardiopulmonary bypass at 37 °C. Three sodium chloride zero balance ultrafiltration bags containing 50 mEq sodium bicarbonate and 0.5 g calcium carbonate are infused. Arterial blood gas measurements are obtained every 15 minutes after every zero balance ultrafiltration bag is infused, and blood is transfused as needed to maintain hemoglobin greater than 8 mg/dL. Cardiopulmonary bypass is weaned with concurrent hemodynamic and transesophageal echocardiogram evaluation of the donor heart. The remainder of the procurement, including the abdominal organs, proceeds in a similar controlled fashion as is performed for a standard donation after brain death donor.
Results: Between January 2020 and May 2022, 18 donation after cardiac death transplants using the thoraco-abdominal normothermic regional perfusion protocol were performed at our institution. The median donor age was 42.5 years (range, 20-51 years), and 88.9% (16/18) were male. The mean total donor cardiopulmonary bypass time was 88.8 ± 51.8 minutes. At the beginning of cardiopulmonary bypass, the average donor lactate was 9.4 ± 1.5 mmol/L compared with an average final lactate of 5.3 ± 2.7 mmol/L (P<.0001). The average beginning potassium was 6.5 ± 1.8 mmol/L compared with an average end potassium of 4.2 ± 0.4 mmol/L (P<.0001) . The average beginning hemoglobin was 6.8 ± 0.7 g/dL, and the average end hemoglobin was 8.2 ± 1.3 g/dL (P<.001) . On average, donation after cardiac death donors received transfusions of 2.3 ± 1.5 units of packed red blood cells. Of the 18 donors who underwent normothermic regional perfusion, all hearts were deemed suitable for recovery and successfully transplanted, a yield of 100%. Other organs successfully recovered and transplanted include kidneys (80.6% yield), livers (66.7% yield), and bilateral lungs (27.8% yield).
Conclusions: The use of cardiopulmonary bypass for thoraco-abdominal normothermic regional perfusion is a burgeoning option for improving the quality of organs from donation after cardiac death donors. Meticulous intraoperative management of donation after cardiac death donors with a specific focus on improving their metabolic milieu may lead to improved graft function in transplant recipients.
Keywords: CIT, cold ischemic time; CPB, cardiopulmonary bypass; DBD, donation after brain death; DCD, donation after circulatory death; DWIT, donor warm ischemic time; ICU, intensive care unit; NRP, normothermic regional perfusion; OPO, Organ Procurement Organization; TEE, transesophageal echocardiography; UF, ultrafiltration; WLST, withdrawal of life-sustaining therapy; Z-BUF, zero-balance ultrafiltration; donation after circulatory death; heart transplantation; normothermic regional perfusion.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- UNOS All-time records again set in 2021 for organ transplants, organ donation from deceased donors. 2022. https://unos.org/news/2021-all-time-records-organ-transplants-deceased-d... Accessed January 2, 2023.
-
- Colvin M., Smith J.M., Ahn Y., Skeans M.A., Messick E., Goff R., et al. OPTN/SRTR 2019 annual data report: heart. Am J Transplant. 2021;21(Suppl 2):356–440. - PubMed
-
- Barnard C.N. The operation. A human cardiac transplant: an interim report of a successful operation performed at Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town. S Afr Med J. 1967;41:1271–1274. - PubMed
-
- Dhital K.K., Chew H.C., Macdonald P.S. Donation after circulatory death heart transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2017;22:189–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous