Outcomes of COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury and longitudinal analysis of laboratory markers during the hospital stay: A multi-center retrospective cohort experience from Pakistan
- PMID: 36820547
- PMCID: PMC9907899
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032919
Outcomes of COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury and longitudinal analysis of laboratory markers during the hospital stay: A multi-center retrospective cohort experience from Pakistan
Abstract
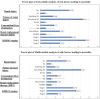
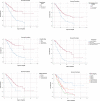
The frequency of acute kidney injury (AKI) in COVID-19 patients can be varied and related to worse outcomes in the disease population. AKI is common among hospitalized patients with COVID-19, particularly the ones needing critical care. This study was conducted in order to determine the outcomes of hospitalized patients with prolonged hospital stays who suffered from COVID-19 associated AKI. It was conducted as a multi-centered, retrospective, cohort study, and including all patients who were diagnosed on COVID-19 PCR. End-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis were excluded. The cohort included 1069 patients, with 68% males, mean age of 56.21 years, and majority within 50 to 75 years age group (60%). Mean disease onset was 14.43 ± 7.44 days and hospital stay was 7.01 ± 5.78 days. About 62% of patients stayed in intensive care and 18% of them were on invasive ventilation. The mortality rate was 27%. Frequency of AKI was 42%, around 14% of them were resolving during hospital stay and other 28% worsened. The mortality rate was significantly higher with AKI (OR: 4.7, P < .001). Alongside AKI, concomitant liver dysfunction was also significantly contributing to mortality (OR: 2.5), apart from ICU stay (OR: 2.9), invasive ventilation (OR: 9.2), and renal replacement therapy (OR: 2.4). Certain laboratory markers were associated with AKI throughout in-hospital stay.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. 2020. World Health Organization. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/ [access date April 22, 2022].
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC COVID data tracker. 2022. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/ [access date April 22, 2022].
-
- Tyrrell DA, Bynoe ML. Cultivation of viruses from a high proportion of patients with colds. Lancet. 1966;1:76–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

