Top 100 most-cited articles on renal cell carcinoma: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36820552
- PMCID: PMC9907913
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032926
Top 100 most-cited articles on renal cell carcinoma: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: To analyze the top 100 most-cited articles on renal cell carcinoma (RCC) using bibliometric methods based on the Web of Science core collection database and to explore the research status, hotspots, and emerging trends in RCC.
Methods: The literature on RCC was searched in the Web of Science core collection database using a specific search strategy, and the types of literature were limited to articles and reviews, with no restrictions to language and publication date. The top 100 articles with the highest number of citations were extracted after the manual screening. The publication year, the number of citations, authors, country, institution, journal, and keywords of these articles were collected and analyzed. Descriptive statistics and visual analysis were performed using Microsoft Excel, VOSviewer, CiteSpace, R, and SPSS.
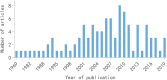
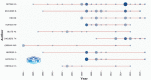
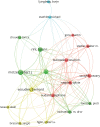
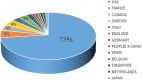
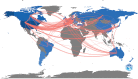
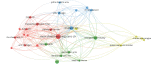
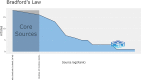
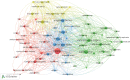
Results: The number of citations of the top 100 articles varied from 541 to 4530, with a median citation count of 807.5, and the citation rates ranged from 13.8 to 448.4 citations per year. Motzer RJ (n = 22), Escudier B (n = 13), Rini BI (n = 13), and Hutson TE (n = 11) were major contributors to this research area, with Motzer RJ publishing 16 articles as the first author. The US (n = 73), France (n = 5), Canada (n = 4), and Sweden (n = 4) were the leading countries for RCC studies. MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENTER (n = 22) was the institution with the highest number of publications. These 100 articles were derived from 24 journals, and the New England Journal of Medicine had the largest number of articles published (n = 18, impact factor = 91.245). The keyword co-occurrence network analysis showed that research hotspots in this field included molecular mechanisms of RCC development and progression, surgical treatment, targeted drug-related clinical trials, and immunotherapy.
Conclusion: We analyzed the top 100 articles with the highest number of citations in the field of RCC and identified the influential authors, countries, institutions, and journals in this field. This study also presented the current research status, hotspots, and future trends in RCC.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evolutions in the management of non-small cell lung cancer: A bibliometric study from the 100 most impactful articles in the field.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;12:939838. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939838. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36059661 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives and trends of CD39-CD73-eAdo/A2aR research in tumor microenvironment: a bibliometric analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1427380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1427380. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39188712 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace from 2000 to 2022.Urol Int. 2023;107(8):755-771. doi: 10.1159/000531322. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Urol Int. 2023. PMID: 37454653 Review.
-
Research hotspots and frontiers of machine learning in renal medicine: a bibliometric and visual analysis from 2013 to 2024.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):907-928. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04259-3. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39472403 Review.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
Cited by
-
Synthetic data as an investigative tool in hypertension and renal diseases research.World J Methodol. 2025 Mar 20;15(1):98626. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i1.98626. eCollection 2025 Mar 20. World J Methodol. 2025. PMID: 40115405 Free PMC article.
-
The bibliometric analysis of most cited 100 papers in anesthesia-induced neurotoxicity.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36508. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036508. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050226 Free PMC article.
-
Renal cell carcinoma and macrophage research: A bibliometric analysis (2004-2023).Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40954. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040954. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, et al. . Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-updagger. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:706–20. - PubMed
-
- Gray RE, Harris GT. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99:179–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

