The tumor biological significance of RNF43 and LRP1B in gastric cancer is complex and context-dependent
- PMID: 36823311
- PMCID: PMC9950470
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-30294-8
The tumor biological significance of RNF43 and LRP1B in gastric cancer is complex and context-dependent
Abstract
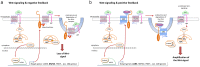
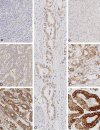
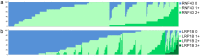
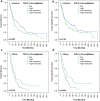
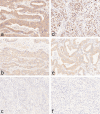
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most common cancer in the world with a poor prognosis. Both RNF43 and LRP1B function as tumor suppressors in the Wnt signaling pathway and have been described to be frequently mutated in GC. In this study of a large and well characterized cohort of 446 GCs we explored the significance of expression of RNF43 and LRP1B and their correlations with clinicopathological patient characteristics. Immunostaining of whole mount tissue sections was documented with the histoscore. Dichotomized at the median, we separated the cohort into a low/negative and a high/positive group of RNF43 and LRP1B expression, respectively. Apart from the entire cohort, we also examined the intestinal and diffuse type GCs separately. Regarding the entire cohort, the expression of RNF43 and LRP1B correlated significantly with the Lauren phenotype and with each other. Interestingly, differences were noted regarding RNF43 between the intestinal and diffuse type GCs. Survival analysis of the intestinal type GCs showed that RNF43 low/negative GCs tended to have a better outcome compared with RNF43 high/positive GCs [24.5 months overall survival (OS) and 25.0 months tumor-specific survival (TSS) vs. 14.1 months OS and 17.9 months TSS, respectively]. To the contrary, diffuse type GCs with RNF43 low/negative had a worse outcome compared with RNF43 high/positive GCs (12.9 months OS and 18.2 months TSS vs. 17.1 months OS and 21.5 months TSS, respectively). On multivariate analysis, RNF43 low/negative versus high/positive was an independent prognosticator of survival in diffuse type GC (hazard ratio 2.393 for OS and 2.398 for TSS). These data support the contention that the expression and biological effect of RNF43 and LRP1B in GC is context-dependent.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of endogenous RNF43 function enhances proliferation and tumour growth of intestinal and gastric cells.Carcinogenesis. 2019 Jun 10;40(4):551-559. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy152. Carcinogenesis. 2019. PMID: 30380024
-
Prognostic significance of LDL receptor-related protein 1B in patients with gastric cancer.J Mol Histol. 2021 Apr;52(2):165-172. doi: 10.1007/s10735-020-09932-2. Epub 2021 Jan 3. J Mol Histol. 2021. PMID: 33389427
-
Frequent frameshift mutations in 2 mononucleotide repeats of RNF43 gene and its regional heterogeneity in gastric and colorectal cancers.Hum Pathol. 2015 Nov;46(11):1640-6. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Hum Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26297255
-
Post-translational Wnt receptor regulation: Is the fog slowly clearing?: The molecular mechanism of RNF43/ZNRF3 ubiquitin ligases is not yet fully elucidated and still controversial.Bioessays. 2021 Apr;43(4):e2000297. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000297. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Bioessays. 2021. PMID: 33569855 Review.
-
LRP1B: A Giant Lost in Cancer Translation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;14(9):836. doi: 10.3390/ph14090836. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt Pathway-Targeted Therapy in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Integrating Benchside Insights with Bedside Applications.Cells. 2025 Jan 24;14(3):178. doi: 10.3390/cells14030178. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Issues with RNF43 antibodies to reliably detect intracellular location.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 6;18(4):e0283894. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283894. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37023034 Free PMC article.
-
Proof of Concept for Genome Profiling of the Neurofibroma/Sarcoma Sequence in Neurofibromatosis Type 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10822. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910822. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409151 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Finger Proteins in the War on Gastric Cancer: Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Potential.Cells. 2023 May 4;12(9):1314. doi: 10.3390/cells12091314. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic events stratifying prognosis of early gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2024 Nov;27(6):1189-1200. doi: 10.1007/s10120-024-01536-z. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Gastric Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39028418 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

