Osteoarticular tuberculosis cases in the southwest of China: A 9-year retrospective study
- PMID: 36824612
- PMCID: PMC9941672
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1051620
Osteoarticular tuberculosis cases in the southwest of China: A 9-year retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Osteoarticular tuberculosis (TB) is an uncommon form of extrapulmonary TB. In this study, we analyzed the epidemiological characteristics, common sites, and drug resistance profiles of osteoarticular TB infections occurring in southwest China.
Methods: A total of 3,254 cases of patients clinically diagnosed with osteoarticular TB infections between 2013 and 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients' demographic and clinical characteristics were collected. Drug sensitivity testing was performed using the microporous plate ratio method. Chi-squared analysis was used to analyze the rates of and trends in mycobacterial isolates.
Results: Of the 3,254 patients, 1,968 (60.5%) were men and boys, and 1,286 (39.5%) were women and girls; patients' ages ranged from 1 to 91 years, with an average of 42 ± 19.3 years. In terms of disease, 2,261 (69.5%) had spinal TB, mainly thoracic (815, 36%) or lumbar (1,080, 48%); joint TB was found in 874 cases (26.9%), mainly occurring in the knee (263, 30%) or hip (227, 26%); and both spinal and joint TB were observed in 119 cases (3.7%). Drug susceptibility tests were performed on 241 isolated strains of MTB; 70 strains (29.0%) were resistant to at least one drug, and MDR-TB and XDR-TB were observed in 7.1 and 1.2% of strains, respectively.
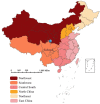
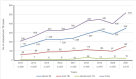
Conclusions: In southwest China over this period, osteoarticular TB mainly affected middle-aged and young men with poor nutritional status. Patients from ethnic minority areas also accounted for a large proportion of cases. Spinal TB is prone to occur in the lumbar and thoracic vertebrae, and joint TB is prone to occur in the lower limb joints. Additionally, there has been an increasing trend in the number of TB cases over the past 9 years, and drug resistance has also increased.
Keywords: clinical characteristics; drug resistance; epidemiology; osteoarticular; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, An, Yang, Liao and Jian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidemiology of skeletal tuberculosis in Beijing, China: a 10-year retrospective analysis of data.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;39(11):2019-2025. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03924-6. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32556926
-
Drug Resistance Characteristics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates From Patients With Tuberculosis to 12 Antituberculous Drugs in China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Nov 5;9:345. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00345. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31828045 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoarticular tuberculosis in Central India: Changing epidemiological profile and emerging challenges.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2023 Jan-Mar;12(1):28-32. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_233_22. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2023. PMID: 36926759
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Trends in drug-resistant tuberculosis in China: data from a clinical tuberculosis centre.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2017 Sep 1;21(9):990-995. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.17.0086. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2017. PMID: 28826447 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma metabolomic analysis reveals the metabolic characteristics and potential diagnostic biomarkers of spinal tuberculosis.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 22;10(7):e27940. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27940. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38571585 Free PMC article.
-
A ten-year experience of musculoskeletal tuberculosis at a tertiary care hospital in South India.J Orthop. 2024 May 3;56:92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2024.05.001. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38800587
-
Prevalence and related factors of TB/HIV co-infection among hospitalized children with tuberculosis in Southwest China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 11;15:1571291. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1571291. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40568707 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis on the epidemiological and drug resistance characteristics of osteoarticular tuberculosis in South-central China.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 30;12:1432071. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1432071. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39281085 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and surgical treatment comparison of multisegmental spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 19;12:1541745. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1541745. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40046928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report 2021 . Geneva, Switzerland: WHO (2021). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021 (accessed December 27, 2021).
-
- WHO: Tuberculosis (TB) . (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-work/laboratory/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

