SATISFACTION OF PARTURIENTS WITH EPIDURAL ANALGESIA DURING DELIVERY: ANALYSIS OF QUESTIONNAIRE AT A SINGLE HOSPITAL CENTER
- PMID: 36824645
- PMCID: PMC9942471
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.s2.01
SATISFACTION OF PARTURIENTS WITH EPIDURAL ANALGESIA DURING DELIVERY: ANALYSIS OF QUESTIONNAIRE AT A SINGLE HOSPITAL CENTER
Abstract
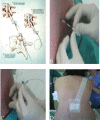
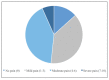
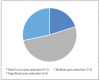
Epidural analgesia is one of the most common methods of relieving labor pain. The objective of this study was to examine the effectiveness of epidural analgesia, maternal satisfaction and relationship between the effectiveness of epidural analgesia and various factors. Data were analyzed retrospectively and collected during 2022. A total of 60 parturients participated in the study. Data were collected through a questionnaire before the parturient was discharged from the hospital. The mean assessment of pain on a 1-10 numeric rating scale before epidural analgesia was 7.7 and 3.4 after administration of epidural analgesia. The median assessment of pain before epidural analgesia was 8 (7¬¬-8), and the median assessment of pain after epidural analgesia was 3 (2-5). The average satisfaction with epidural analgesia on a 1-10 scale was 8.11, and the median satisfaction was 10 (7-10). Total of 35 (58.3%) parturients rated satisfaction with 10. Statistically significant association between the effectiveness of epidural analgesia and parity, dilution of administered levobupivacaine, fentanyl administration, and level of education was not found. Childbirth pain is significantly alleviated by the application of epidural analgesia and the satisfaction of parturients is very high.
Keywords: effectiveness of epidural analgesia; epidural analgesia; labor pain relief; maternal satisfaction.
Figures
References
-
- Wall PD, Melzack R. Wall and Melzack’s textbook of pain. 6th ed. McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M,Tracey I, Turk DC, editors. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2013. p. 772-93
-
- Chestnut D. Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. 6th ed. Chestnut D, Wong C, Tsen L, Ngan Kee W, Beilin Y, Myhre J, editors. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2019.
-
- Bartolek D, Šakić, K. Bezboni porod// Medix,10 (2004), 54/55; 133-134
-
- Van de Velde M. Modern neuraxial labor analgesia: options for initiation, maintenance and drug selection. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2009;56:546–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources