An unusual case of colonic duplication cyst in an adult with dysplasia
- PMID: 36824693
- PMCID: PMC9943052
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjad039
An unusual case of colonic duplication cyst in an adult with dysplasia
Erratum in
-
Correction to: An unusual case of colonic duplication cyst in an adult with dysplasia.J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Mar 15;2023(3):rjad150. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjad150. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36937797 Free PMC article.
Abstract
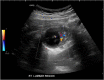
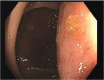
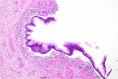
Duplication cysts are rare benign congenital malformations typically identified in children by the age of 2 years. We report a rare case of colonic duplication cyst with dysplasia in an adult. A 32-year-old male was diagnosed with non-specific abdominal symptoms. Abdominopelvic computed tomography scan demonstrated a submucosal cystic lesion in the right colon. He underwent laparoscopic right hemicolectomy. Histopathology showed colonic duplication cyst with low grade dysplasia. He is due for a surveillance colonoscopy in 3 years. Duplication cyst in an adult colon with dysplasia is extremely rare. They are usually present in the terminal ileum. They have non-specific abdominal symptoms or can be asymptomatic. They are often identified incidentally or intraoperatively. Imaging may demonstrate a cystic lesion. Histopathology is required for definitive diagnosis. There are no guidelines or consensus on managing duplication cysts in adults. We recommend an oncological resection of the involved colon. Surveillance with routine colonoscopy is advisable.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. © The Author(s) 2023.
Figures





References
-
- Radhakrishnan L, George J, Abraham LK. Right sided colonic duplication cyst with malignant twist in a young adult—a case report. J Gastrointest Cancer 2022;53:805–8. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez Garcia P, Sanchez Perez A, Romera Barba E, Calero Garcia P, Gonzalez-Costea MR. Colonic duplication cyst in adult. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;43:360–1. - PubMed
-
- Hsu H, Gueng MK, Tseng YH, Wu CC, Liu PH, Chen CCC. Adenocarcinoma arising from colonic duplication cyst with metastasis to omentum: a case report. J Clin Ultrasound 2011;39:41–3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

