This is a preprint.
Immunotherapy Responsiveness and Risk of Relapse in Down Syndrome Regression Disorder
- PMID: 36824719
- PMCID: PMC9949176
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2521595/v1
Immunotherapy Responsiveness and Risk of Relapse in Down Syndrome Regression Disorder
Update in
-
Immunotherapy responsiveness and risk of relapse in Down syndrome regression disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Aug 8;13(1):276. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02579-z. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37553347 Free PMC article.
Abstract
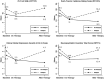
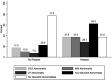
Down syndrome regression disorder (DSRD) is a clinical symptom cluster consisting of neuropsychiatric regression without an identifiable cause. This study evaluated the clinical effectiveness of IVIg and evaluated clinical characteristics associated with relapse after therapy discontinuation. A prospective, multi-center, non-randomized, observational study was performed. Patients met criteria for DSRD and were treated with IVIg. All patients underwent a standardized wean off therapy after 9-12 months of treatment. Baseline, on therapy, and relapse scores of the Neuropsychiatric Inventory Total Score (NPITS), Clinical Global Impression-Severity (CGI-S), and the Bush-Francis Catatonia Rating Scale (BFCRS) were used to track clinical symptoms. Eighty-two individuals were enrolled in this study. Patients had lower BFCRS (MD: -6.68; 95% CI: -8.23, -5.14), CGI-S (MD: -1.27; 95% CI: -1.73, -0.81), and NPITS scores (MD: -6.50; 95% CI: -7.53, -5.47) while they were on therapy compared to baseline. Approximately 46% of the patients (n = 38) experienced neurologic relapse with wean of IVIg. Patients with neurologic relapse were more likely to have any abnormal neurodiagnostic study (χ2 = 11.82, p = 0.001), abnormal MRI (χ2 = 7.78, p = 0.005), and abnormal LP (χ2 = 5.45, p = 0.02), and a personal history of autoimmunity (OR: 6.11, p < 0.001) compared to patients without relapse. IVIg was highly effective in the treatment of DSRD. Individuals with a history of personal autoimmunity or neurodiagnostic abnormalities were more likely to relapse following weaning of immunotherapy, indicating the potential for, a chronic autoimmune etiology in some cases of DSRD.
Figures

References
-
- de Graaf G, Buckley F, Skotko BG. Estimates of the live births, natural losses, and elective terminations with Down syndrome in the United States. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167a(4):756–767. - PubMed
-
- Rosso M, Fremion E, Santoro SL, et al. Down Syndrome Disintegrative Disorder: A Clinical Regression Syndrome of Increasing Importance. Pediatrics. 2020;145(6). - PubMed
-
- Santoro SL, Cannon S, Capone G, et al. Unexplained regression in Down syndrome: 35 cases from an international Down syndrome database. Genet Med. 2020;22(4):767–776. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

