This is a preprint.
Interleukin 31 receptor alpha augments muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 3-driven calcium signaling and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma
- PMID: 36824812
- PMCID: PMC9949265
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2564484/v1
Interleukin 31 receptor alpha augments muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 3-driven calcium signaling and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma
Update in
-
Interleukin 31 receptor α promotes smooth muscle cell contraction and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 11;14(1):8207. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44040-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38081868 Free PMC article.
Abstract
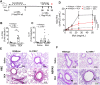
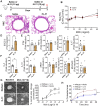
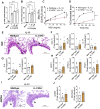
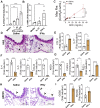
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), inflammation, and goblet cell hyperplasia. Both Th1 and Th2 cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-13 have been shown to induce asthma; however, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. We observed a significant increase in the expression of IL-31RA, but not its cognate ligand IL-31 during allergic asthma. In support of this, IFN-γ and Th2 cytokines, IL-4 and IL-13, upregulated IL-31RA but not IL-31 in airway smooth muscle cells (ASMC). Importantly, the loss of IL-31RA attenuated AHR but had no effects on inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia in allergic asthma or mice treated with IL-13 or IFN-γ. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that IL-31RA functions as a positive regulator of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 3 expression and calcium signaling in ASMC. Together, these results identified a novel role for IL-31RA in AHR distinct from airway inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia in asthma.
Keywords: airway hyperresponsiveness; allergic asthma; calcium signaling; interleukin 31; lung.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

