This is a preprint.
Ketogenic diet promotes tumor ferroptosis but induces relative corticosterone deficiency that accelerates cachexia
- PMID: 36824830
- PMCID: PMC9949105
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.02.17.528937
Ketogenic diet promotes tumor ferroptosis but induces relative corticosterone deficiency that accelerates cachexia
Update in
-
Ketogenic diet promotes tumor ferroptosis but induces relative corticosterone deficiency that accelerates cachexia.Cell Metab. 2023 Jul 11;35(7):1147-1162.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.05.008. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Cell Metab. 2023. PMID: 37311455 Free PMC article.
Abstract
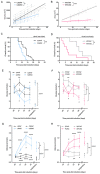
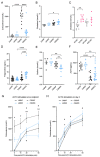
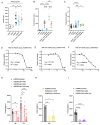
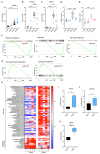
The dependency of cancer cells on glucose can be targeted with high-fat low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet (KD). However, hepatic ketogenesis is suppressed in IL-6 producing cancers, which prevents the utilization of this nutrient source as energy for the organism. In two IL-6 associated murine models of cancer cachexia we describe delayed tumor growth but accelerated onset of cancer cachexia and shortened survival when mice are fed KD. Mechanistically, we find this uncoupling is a consequence of the biochemical interaction of two simultaneously occurring NADPH-dependent pathways. Within the tumor, increased production of lipid peroxidation products (LPPs) and, consequently, saturation of the glutathione (GSH) system leads to ferroptotic death of cancer cells. Systemically, redox imbalance and NADPH depletion impairs the biosynthesis of corticosterone, the main regulator of metabolic stress, in the adrenal glands. Administration of dexamethasone, a potent glucocorticoid, improves food intake, normalizes glucose homeostasis and utilization of nutritional substrates, delays onset of cancer cachexia and extends survival of tumor-bearing mice fed KD, while preserving reduced tumor growth. Our study highlights that the outcome of systemic interventions cannot necessarily be extrapolated from the effect on the tumor alone, but that they have to be investigated for anti-cancer and host effects. These findings may be relevant to clinical research efforts that investigate nutritional interventions such as KD in patients with cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alborzinia Hamed, Flórez Andrés F., Kreth Sina, Brückner Lena M., Yildiz Umut, Gartlgruber Moritz, Odoni Dorett I., Poschet Gemot, Garbowicz Karolina, Shao Chunxuan, Klein Corinna, Meier Jasmin, Zeisberger Petra, Nadler-Holly Michal, Ziehm Matthias, Paul Franziska, Burhenne Jürgen, Bell Emma, Shaikhkarami Marjan, Würth Roberto, Stainczyk Sabine A., Wecht Elisa M., Kreth Jochen, Büttner Michael, Ishaque Naveed, Schlesner Matthias, Nicke Barbara, Stresemann Carlo, Llamazares-Prada María, Reiling Jan H., Fischer Matthias, Amit Ido, Selbach Matthias, Herrmann Carl, Wölfl Stefan, Henrich Kai Oliver, Höfer Thomas, Trumpp Andreas, and Westermann Frank. 2022. “MYCN Mediates Cysteine Addiction and Sensitizes Neuroblastoma to Ferroptosis.” Nature Cancer 3(4):471–85. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arbour Kathryn C., Mezquita Laura, Long Niamh, Rizvi Hira, Auclin Edouard, Ni Andy, Martínez-Bernal Gala, Ferrara Roberto, Lai W. Victoria, Hendriks Lizza E. L., Sabari Joshua K., Caramella Caroline, Plodkowski Andrew J., Halpenny Darragh, Chaft Jamie E., Planchard David, Riely Gregory J., Besse Benjamin, and Hellmann Matthew D.. 2018. “Impact of Baseline Steroids on Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients with Non–Small–Cell Lung Cancer.” Journal of Clinical Oncology 36(28):2872–78. - PubMed
-
- Badgley Michael A., Kremer Daniel M., Maurer H. Carlo, DelGiorno Kathleen E., Lee Ho Joon, Purohit Vinee, Sagalovskiy Irina R., Ma Alice, Kapilian Jonathan, Firl Christina E. M., Decker Amanda R., Sastra Steve A., Palermo Carmine F., Andrade Leonardo R., Sajjakulnukit Peter, Zhang Li, Tolstyka Zachary P., Hirschhorn Tal, Lamb Candice, Liu Tong, Gu Wei, Seeley E. Scott, Stone Everett, Georgiou George, Manor Uri, luga Alina, Wahl Geoffrey M., Stockwell Brent R., Lyssiotis Costas A., and Olive Kenneth P.. 2020. “Cysteine Depletion Induces Pancreatic Tumor Ferroptosis in Mice.” Science 368(6486):85–89. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
