Bioinformatics analysis and consistency verification of a novel tuberculosis vaccine candidate HP13138PB
- PMID: 36825009
- PMCID: PMC9942524
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1102578
Bioinformatics analysis and consistency verification of a novel tuberculosis vaccine candidate HP13138PB
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Bioinformatics analysis and consistency verification of a novel tuberculosis vaccine candidate HP13138PB.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 8;14:1154693. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1154693. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36845146 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: With the increasing incidence of tuberculosis (TB) and the shortcomings of existing TB vaccines to prevent TB in adults, new TB vaccines need to be developed to address the complex TB epidemic.
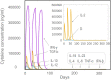
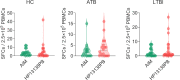
Method: The dominant epitopes were screened from antigens to construct a novel epitope vaccine termed HP13138PB. The immune properties, structure, and function of HP13138PB were predicted and analyzed with bioinformatics and immunoinformatics. Then, the immune responses induced by the HP13138PB were confirmed by enzyme-linked immunospot assay (ELISPOT) and Th1/Th2/Th17 multi-cytokine detection kit.
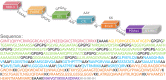
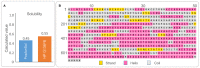
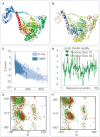
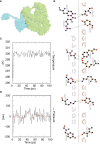
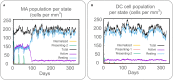
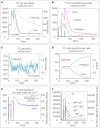
Result: The HP13138PB vaccine consisted of 13 helper T lymphocytes (HTL) epitopes, 13 cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) epitopes, and 8 B-cell epitopes. It was found that the antigenicity, immunogenicity, and solubility index of the HP13138PB vaccine were 0.87, 2.79, and 0.55, respectively. The secondary structure prediction indicated that the HP13138PB vaccine had 31% of α-helix, 11% of β-strand, and 56% of coil. The tertiary structure analysis suggested that the Z-score and the Favored region of the HP13138PB vaccine were -4.47 88.22%, respectively. Furthermore, the binding energies of the HP13138PB to toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) was -1224.7 kcal/mol. The immunoinformatics and real-world experiments showed that the HP13138PB vaccine could induce an innate and adaptive immune response characterized by significantly higher levels of cytokines such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-4 (IL-4), and IL-10.
Conclusion: The HP13138PB is a potential vaccine candidate to prevent TB, and this study preliminarily evaluated the ability of the HP13138PB to generate an immune response, providing a precursor target for developing TB vaccines.
Keywords: bioinformatics; epitope vaccines; immune responses; immunoinformatics; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Cheng, Jiang, Wang, Wang, Xue, Wang and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization: Genevapp: World Health Organization; (2022).
-
- Huang F, Zhao Y. Global control of tuberculosis: Current status and future prospects. In: Zoonoses (2021) 2:21. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2021-0021 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

