Soluble IgE-binding factors in the serum of food-allergic patients: Possible pathophysiological role of soluble FcεRI as protective factor
- PMID: 36825516
- PMCID: PMC9904993
- DOI: 10.1002/clt2.12222
Soluble IgE-binding factors in the serum of food-allergic patients: Possible pathophysiological role of soluble FcεRI as protective factor
Abstract
Background: IgE-mediated food allergy is the result of an aberrant immune response involving the interaction of a food allergen with its specific IgE bound to FcɛRI, the high affinity IgE receptor, on mast cells. Allergen-specific IgE also binds to soluble binding factors, but, their expression and role in food allergy is not well characterized. Here, we assess the prevalence and relevance of soluble IgE binding factors in food allergy and tolerance.
Methods: We measured serum levels of four IgE binding factors, that is, galectin-3, galectin-9, soluble FcɛRI (sFcεRI) and soluble CD23 (sCD23) in 67 adults sensitized to peanut or hazelnut and sFcɛRI in 29 children sensitized to hen's egg. Adults without food allergen sensitization (n = 17) served as healthy controls. We compared serum levels of patients and controls and assessed them, in the former, for links to clinical features including allergy and tolerance.
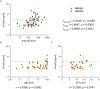
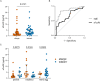
Results: Serum levels of sFcɛRI and sCD23, but not galectin-3 and galectin-9, significantly differ in food-sensitized patients as compared to healthy controls. A subgroup (28%) of peanut and hazelnut allergic patients had elevated sFcεRI levels, that were associated with higher total and specific IgE levels. Furthermore, sFcεRI levels were significantly higher in tolerant subjects compared to allergics. Among hazelnut allergic patients, those with high sFcεRI levels tolerated the highest protein amounts in the oral food challenge.
Conclusion: sFcɛRI but not sCD23, galectin-3 and galectin-9 might play a role in the pathophysiology of food allergy. Its functional role or use as biomarker should be assessed in further studies.
Keywords: CD23; FcεRI; IgE receptor; food allergy; galectin-3; galectin-9.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Carolin Steinert: No conflict of interests. Sherezade Moñino‐Romero: No conflict of interests. Monique Butze: No conflict of interests. Jörg Scheffel: No conflict of interests in relation to this paper. Outside of it JS has conducted studies for, received research funds/was advisor for Allakos, Ascilion, AstraZeneca, CSL Behring, Escient, Novartis, Sanofi, Third Harmonic Bio, ThirdRock, ThermoFisher. Sabine Dölle‐Bierke: No conflict of interests. Josefine Dobbertin‐Welsch: No conflict of interests. Kirsten Beyer: No conflict of interests in relation to this paper. Outside of it, KB received personal fee from Aimmune, Bencard, Danone, DBV, Hipp, Hycor, Jenapharma, Infectopharm, Mylan/Meda, Nestle, Novartis and ThermoFisher. Marcus Maurer: No conflict of interest in relation to this paper. Outside of it, MM is or recently was a speaker and/or advisor for and/or has received research funding from Allakos, Amgen, Aralez, ArgenX, AstraZeneca, Celldex, Centogene, CSL Behring, FAES, Genentech, GIInnovation, GSK, Innate Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Menarini, Moxie, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Regeneron, Third Harmonic Bio, UCB, and Uriach. Sabine Altrichter: No conflict of interest in relation to this paper. Outside of it, SA has conducted studies for/was advisor for/was speaker for AstraZeneca, Allakos, ALK, CSLBehring, LeoPharma, Moxie, Novartis, Sanofi, Takeda, Thermofisher.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The soluble isoform of human FcɛRI is an endogenous inhibitor of IgE-mediated mast cell responses.Allergy. 2019 Feb;74(2):236-245. doi: 10.1111/all.13567. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30030936 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble IgE receptors--elements of the IgE network.Immunol Lett. 2011 Dec 30;141(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.08.004. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Immunol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21920387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble CD23 in allergic diseases.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 1999;47(4):251-5. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 1999. PMID: 10483874
-
A soluble form of the high affinity IgE receptor, Fc-epsilon-RI, circulates in human serum.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 22;6(4):e19098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019098. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21544204 Free PMC article.
-
The rationale for development of ligelizumab in food allergy.World Allergy Organ J. 2022 Sep 13;15(9):100690. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2022.100690. eCollection 2022 Sep. World Allergy Organ J. 2022. PMID: 36185545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin 9 rescues the inducibility of IL-10 expression in regulatory B cells of patients with food allergy.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84079-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747510 Free PMC article.
-
CAR-NKT Cells in Asthma: Use of NKT as a Promising Cell for CAR Therapy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Jun;66(3):328-362. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08998-0. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38995478 Review.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of YH35324 on FcεRIα-Mediated Mast Cell/Basophil Activation.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2025 Mar;17(2):181-195. doi: 10.4168/aair.2025.17.2.181. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 40204504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osborne NJ, Koplin JJ, Martin PE, et al. Prevalence of challenge‐proven IgE‐mediated food allergy using population‐based sampling and predetermined challenge criteria in infants. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(3):668‐676.e1‐2. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Muñoz‐Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001–2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119(4):1016‐1018. - PubMed
-
- Colver AF, Nevantaus H, Macdougall CF, Cant AJ. Severe food‐allergic reactions in children across the UK and Ireland, 1998–2000. Acta Paediatr 2005;94(6):689‐695. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

