Individual Heterogeneity in the Relations Between Sleep, Inflammation, and Somatic Symptoms
- PMID: 36825926
- PMCID: PMC10082064
- DOI: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000001175
Individual Heterogeneity in the Relations Between Sleep, Inflammation, and Somatic Symptoms
Abstract
Objective: Poor sleep is associated with the experience of more somatic symptoms and a proinflammatory state, whereas a proinflammatory state may also result in the experience of more somatic symptoms. However, existing studies ignore individual differences in these associations. We aimed to study relations between sleep, inflammatory markers, and somatic symptoms at a within-individual level.
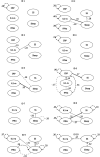
Methods: Time series of daily data on sleep, somatic symptoms, and inflammation markers in 10 healthy individuals (age, 19-58 years; three men) for 63 days were analyzed. Bidirectional lagged ( t - 1) and contemporaneous ( t ) relations between sleep duration, inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein, interferon-α, interleukin 1RA), and somatic symptoms were analyzed using 24-hour urine and diary data. Unified structural equation modeling was used to analyze the association between sleep duration, the three inflammatory markers, and the amount of somatic symptoms at the individual level.
Results: Associations were found between sleep and at least one of three inflammatory markers in four individuals, both positive (three associations) and negative (five associations) and contemporaneous (four associations) and lagged (four associations). Sleep was related to somatic symptoms in four individuals, both positive ( n = 2) and negative ( n = 2) and contemporaneous ( n = 3) and lagged ( n = 1). Inflammatory markers were associated with somatic symptoms in three individuals, both positive (three associations) and negative (one association) and contemporaneous (three associations) and lagged (one associations). Two individuals showed no associations between sleep, inflammatory markers, and somatic symptoms.
Conclusions: We observed a large variability in presence, strength, and direction of associations between sleep, inflammatory markers, and somatic symptoms.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Psychosomatic Society.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang J Lam SP Li SX Tang NL Yu MWM Li AM, et al. . Insomnia, sleep quality, pain, and somatic symptoms: sex differences and shared genetic components. Pain 2012;153:666–73. - PubMed
-
- Bonvanie IJ, Oldehinkel AJ, Rosmalen JGM, Janssens KAM. Sleep problems and pain: a longitudinal cohort study in emerging adults. Pain 2016;157:957–63. - PubMed
-
- Cappuccio FP, Cooper D, D’Elia L, Strazzullo P, Miller MA. Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Eur Heart J 2011;32:1484–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

