Inspiratory-Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial
- PMID: 36825943
- PMCID: PMC9952421
- DOI: 10.3390/arm91010009
Inspiratory-Expiratory Muscle Training Improved Respiratory Muscle Strength in Dialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomised Trial
Abstract
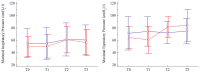
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) exposes patients to progressive physical deconditioning involving the respiratory muscles. The aim of this pilot randomized controlled trial was to determine the feasibility and effectiveness of low-intensity respiratory muscle training (RMT) learned at the hospital and performed at home. A group of ESKD patients (n = 22) were randomized into RMT or usual care (control group, CON) in a 1:1 ratio. The respiratory training was performed at home with an inspiratory-expiratory system for a total of 5 min of breathing exercises in a precise rhythm (8 breaths per minute) interspersed with 1 min of rest, two times per day on nondialysis days for a total of 4 weeks, with the air resistance progressively increasing. Outcome measures were carried out every 4 weeks for 3 consecutive months, with the training executed from the 5th to the 8th week. Primary outcomes were maximal inspiratory and expiratory pressure (MIP, MEP), while secondary outcomes were lung capacity (FEV1, FVC, MVV). Nineteen patients without baseline between-group differences completed the trial (T: n = 10; Age: 63 ± 10; Males: n = 12). Both MIP and MEP significantly improved at the end of training in the T group only, with a significant difference of MEP of 23 cmH2O in favor of the RMT group (p = 0.008). No significant variations were obtained for FVC, FEV1 or MVV in either group, but there was a greater decreasing trend over time for the CON group, particularly for FVC (t = -2.00; p = 0.046). Low-fatiguing home-based RMT, with a simple device involving both inspiratory and expiratory muscles, may significantly increase respiratory muscle strength.
Keywords: dialysis; end-stage kidney disease; exercise; rehabilitation; respiratory muscle training; respiratory muscles; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
Annalisa Cogo and Fabio Manfredini previously received a grant from MEDINET. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- De Medeiros A.I.C., Fuzari H.K.B., Rattesa C., Brandão D.C., de Melo Marinho P.É. Inspiratory muscle training improves respiratory muscle strength, functional capacity and quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2017;63:76–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2017.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manfredini F., Mallamaci F., D’Arrigo G., Baggetta R., Bolignano D., Torino C., Lamberti N., Bertoli S., Ciurlino D., Rocca-Rey L., et al. Exercise in Patients on Dialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017;28:1259–1268. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016030378. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pomidori L., Lamberti N., Malagoni A.M., Manfredini F., Pozzato E., Felisatti M., Catizone L., Barillà A., Zuccalà A., Tripepi G., et al. Respiratory muscle impairment in dialysis patients: Can minimal dose of exercise limit the damage? A Preliminary study in a sample of patients enrolled in the EXCITE trial. J. Nephrol. 2016;29:863–869. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0325-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical