Beneficial Effects of Red Wine Polyphenols on Human Health: Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 36825997
- PMCID: PMC9955827
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb45020052
Beneficial Effects of Red Wine Polyphenols on Human Health: Comprehensive Review
Abstract
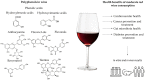
Polyphenols are secondary plant metabolites synthesized during the development of the grape berry as a response to stress conditions. They are important constituents in red wines that contribute to the sensory properties and antioxidant activity of wines. Due to the development of highly sophisticated analytical devices, it is now possible to characterize the structure of highly polymerized polyphenols and obtain a full polyphenol profile of red wines. Red wine polyphenols include the ones present in grapes as well as new polyphenol products formed during the winemaking process. Among them, the most important groups and their representatives are flavanols (catechin), stilbenes (trans-resveratrol), flavonols (quercetin) and hydroxybenzoic acids (gallic acid). It is known that polyphenols exhibit beneficial effects on human health, such as anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic and cardio-protective effects. Many studies have been conducted on the health effects of red wine polyphenols in cancer chemopreventive activities, neuroprotective effects and impact on cardiovascular diseases, gut microbiota in humans, etc. This review will provide major scientific findings on the impact of red wine polyphenols on human health as well as a review of polyphenols present in red wines and their main features.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; chemoprevention effect; gut microbiota; human health; polyphenols; red wine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of the anticarcinogenic properties of four red wine polyphenols.Clin Biochem. 2002 Mar;35(2):119-24. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(02)00275-8. Clin Biochem. 2002. PMID: 11983346
-
Grape and wine polymeric polyphenols: Their importance in enology.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(4):563-579. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1381071. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 28933917 Review.
-
Rosé Sparkling Wines: Influence of Winemaking Practices on the Phytochemical Polyphenol During Aging on Lees and Commercial Storage.J Food Sci. 2018 Nov;83(11):2790-2801. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14379. Epub 2018 Oct 29. J Food Sci. 2018. PMID: 30370927
-
Phenolic characteristics acquired by berry skins of Vitis vinifera cv. Tempranillo in response to close-to-ambient solar ultraviolet radiation are mostly reflected in the resulting wines.J Sci Food Agric. 2020 Jan 15;100(1):401-409. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10068. Epub 2019 Nov 9. J Sci Food Agric. 2020. PMID: 31637723
-
The effects of grape and red wine polyphenols on gut microbiota - A systematic review.Food Res Int. 2018 Nov;113:277-287. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.019. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30195522
Cited by
-
Unraveling the therapeutic efficacy of resveratrol in Alzheimer's disease: an umbrella review of systematic evidence.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024 Mar 19;21(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12986-024-00792-1. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38504306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Oxidative Stress in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;13(12):1462. doi: 10.3390/antiox13121462. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol or No Alcohol in Wine: Half a Century of Debate.Foods. 2025 May 23;14(11):1854. doi: 10.3390/foods14111854. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of empirical anti-inflammatory diet index: a cross-sectional study.Nutr J. 2025 Jun 23;24(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12937-025-01165-x. Nutr J. 2025. PMID: 40551133 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases by Wine-Derived Compounds: Implications for Cancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2025 May 28;15(6):781. doi: 10.3390/biom15060781. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pintać D., Bekvalac K., Mimica-Dukić N., Rašeta M., Anđelić N., Lesjak M., Orčić D. Comparison study between popular brands of coffee, tea and red wine regarding polyphenols content and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. Adv. 2022;1:100030. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100030. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources