Phosphonation of Alginate-Polyethyleneimine Beads for the Enhanced Removal of Cs(I) and Sr(II) from Aqueous Solutions
- PMID: 36826322
- PMCID: PMC9957171
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9020152
Phosphonation of Alginate-Polyethyleneimine Beads for the Enhanced Removal of Cs(I) and Sr(II) from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
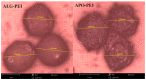
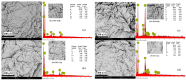
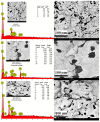
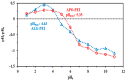
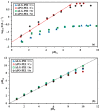
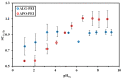
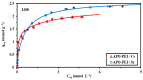
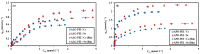
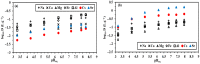
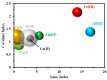
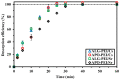
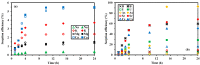
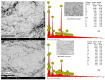
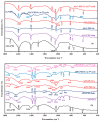
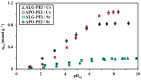
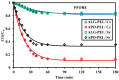
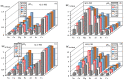
Although Cs(I) and Sr(II) are not strategic and hazardous metal ions, their recovery from aqueous solutions is of great concern for the nuclear industry. The objective of this work consists of designing a new sorbent for the simultaneous recovery of these metals with selectivity against other metals. The strategy is based on the functionalization of algal/polyethyleneimine hydrogel beads by phosphonation. The materials are characterized by textural, thermo-degradation, FTIR, elemental, titration, and SEM-EDX analyses to confirm the chemical modification. To evaluate the validity of this modification, the sorption of Cs(I) and Sr(II) is compared with pristine support under different operating conditions: the pH effect, kinetics, and isotherms are investigated in mono-component and binary solutions, before investigating the selectivity (against competitor metals) and the possibility to reuse the sorbent. The functionalized sorbent shows a preference for Sr(II), enhanced sorption capacities, a higher stability at recycling, and greater selectivity against alkali, alkaline-earth, and heavy metal ions. Finally, the sorption properties are compared for Cs(I) and Sr(II) removal in a complex solution (seawater sample). The combination of these results confirms the superiority of phosphonated sorbent over pristine support with promising performances to be further evaluated with effluents containing radionuclides.
Keywords: cesium; composite hydrogel; functionalization; metal sorption; modeling; reuse cycles; selectivity; sorption isotherm; strontium; uptake kinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
-
- RSC Periodic Table. [(accessed on 5 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/
-
- Fiskum S.K., Colburn H.A., Rovira A.M., Allred J.R., Smoot M.R., Peterson R.A., Landon M.R., Colosi K.A. Cesium removal from AP-105 Hanford tank waste using spherical resorcinol formaldehyde resin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019;54:1932–1941. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2019.1577273. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

