Review on Bioinspired Design of ECM-Mimicking Scaffolds by Computer-Aided Assembly of Cell-Free and Cell Laden Micro-Modules
- PMID: 36826900
- PMCID: PMC9964438
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb14020101
Review on Bioinspired Design of ECM-Mimicking Scaffolds by Computer-Aided Assembly of Cell-Free and Cell Laden Micro-Modules
Abstract
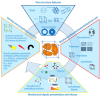
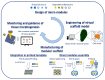
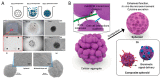
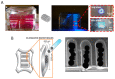
Tissue engineering needs bioactive drug delivery scaffolds capable of guiding cell biosynthesis and tissue morphogenesis in three dimensions. Several strategies have been developed to design and fabricate ECM-mimicking scaffolds suitable for directing in vitro cell/scaffold interaction, and controlling tissue morphogenesis in vivo. Among these strategies, emerging computer aided design and manufacturing processes, such as modular tissue unit patterning, promise to provide unprecedented control over the generation of biologically and biomechanically competent tissue analogues. This review discusses recent studies and highlights the role of scaffold microstructural properties and their drug release capability in cell fate control and tissue morphogenesis. Furthermore, the work highlights recent advances in the bottom-up fabrication of porous scaffolds and hybrid constructs through the computer-aided assembly of cell-free and/or cell-laden micro-modules. The advantages, current limitations, and future challenges of these strategies are described and discussed.
Keywords: CAD scaffold; micro-modules; modular tissue engineering; tissue spheroids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review on Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing of Drug Delivery Scaffolds for Cell Guidance and Tissue Regeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Jun 24;9:682133. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.682133. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34249885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular Strategies to Build Cell-Free and Cell-Laden Scaffolds towards Bioengineered Tissues and Organs.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 1;8(11):1816. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111816. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31683796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated 3D bioassembly of micro-tissues for biofabrication of hybrid tissue engineered constructs.Biofabrication. 2018 Jan 12;10(2):024103. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/aa9ef1. Biofabrication. 2018. PMID: 29199637
-
Hybrid spheroid microscaffolds as modular tissue units to build macro-tissue assemblies for tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2023 Jul 15;165:72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.03.010. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 35288312
-
Modular Tissue Assembly Strategies for Biofabrication of Engineered Cartilage.Ann Biomed Eng. 2017 Jan;45(1):100-114. doi: 10.1007/s10439-016-1609-3. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017. PMID: 27073109 Review.
Cited by
-
From Static to Dynamic: Smart Materials Pioneering Additive Manufacturing in Regenerative Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 30;24(21):15748. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115748. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Coating of Electrospun Nanofibers with Bioactive Molecules for Stem Cell Osteogenesis In Vitro.Cell J. 2024 Feb 1;26(2):130-138. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2024.2008921.1388. Cell J. 2024. PMID: 38459730 Free PMC article.
-
Mimicking osteoid 3D porous dense microfiber silk fibroin embedded poly(vinyl alcohol) scaffold for alveolar ridge preservation.Regen Biomater. 2024 Nov 13;12:rbae130. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae130. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39803357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Netti P.A. Bioactivated Materials for Cell and Tissue Guidance. In: Orlando G., Soker S., Lerut J., Stratta R.J., editors. Regenerative Medicine Applications in Organ Transplantation. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2014. pp. 137–150.
-
- Ozbolat I.T. Scaffold-Based or Scaffold-Free Bioprinting: Competing or Complementing Approaches? J. Nanotechnol. Eng. Med. 2015;6:024701-1. doi: 10.1115/1.4030414. - DOI
-
- Collet C., Asano T., Onuma Y., Miyazaki Y., Tenekecioglu E., Katagiri Y., Puricel S., Kimura T., Gao R., De Winter R., et al. Late thrombotic events after bioresorbable scaffold implantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Eur. Heart J. 2017;38:2559–2564. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx155. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

