The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography
- PMID: 36826969
- PMCID: PMC9962859
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging9020050
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Echocardiography
Abstract
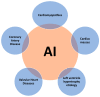
Echocardiography is an integral part of the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease. The use and application of artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly expanding field in medicine to improve consistency and reduce interobserver variability. AI can be successfully applied to echocardiography in addressing variance during image acquisition and interpretation. Furthermore, AI and machine learning can aid in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease. In the realm of echocardiography, accurate interpretation is largely dependent on the subjective knowledge of the operator. Echocardiography is burdened by the high dependence on the level of experience of the operator, to a greater extent than other imaging modalities like computed tomography, nuclear imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging. AI technologies offer new opportunities for echocardiography to produce accurate, automated, and more consistent interpretations. This review discusses machine learning as a subfield within AI in relation to image interpretation and how machine learning can improve the diagnostic performance of echocardiography. This review also explores the published literature outlining the value of AI and its potential to improve patient care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; echocardiography; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

