BDNF/TrkB signaling endosomes in axons coordinate CREB/mTOR activation and protein synthesis in the cell body to induce dendritic growth in cortical neurons
- PMID: 36826992
- PMCID: PMC9977295
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.77455
BDNF/TrkB signaling endosomes in axons coordinate CREB/mTOR activation and protein synthesis in the cell body to induce dendritic growth in cortical neurons
Abstract
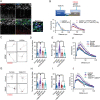
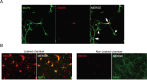
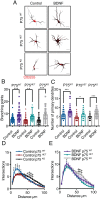
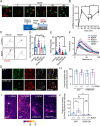
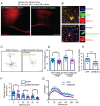
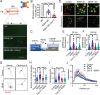
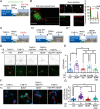
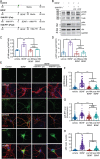
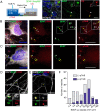
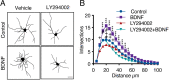
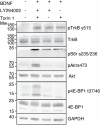
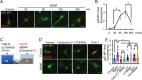
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptors tropomyosin kinase receptor B (TrkB) and the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75) are the primary regulators of dendritic growth in the CNS. After being bound by BDNF, TrkB and p75 are endocytosed into endosomes and continue signaling within the cell soma, dendrites, and axons. We studied the functional role of BDNF axonal signaling in cortical neurons derived from different transgenic mice using compartmentalized cultures in microfluidic devices. We found that axonal BDNF increased dendritic growth from the neuronal cell body in a cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-dependent manner. These effects were dependent on axonal TrkB but not p75 activity. Dynein-dependent BDNF-TrkB-containing endosome transport was required for long-distance induction of dendritic growth. Axonal signaling endosomes increased CREB and mTOR kinase activity in the cell body, and this increase in the activity of both proteins was required for general protein translation and the expression of Arc, a plasticity-associated gene, indicating a role for BDNF-TrkB axonal signaling endosomes in coordinating the transcription and translation of genes whose products contribute to learning and memory regulation.
Keywords: BDNF; CREB; Dynein; TrkB; axonal signaling; dendritic arborization; mTOR; mouse; neuroscience; rat; signaling endosome.
© 2023, Moya-Alvarado et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GM, RT, MI, AA, MG, CW, WM, EP, FB No competing interests declared
Figures



Update of
References
-
- Andres-Alonso M, Ammar MR, Butnaru I, Gomes GM, Acuña Sanhueza G, Raman R, Yuanxiang P, Borgmeyer M, Lopez-Rojas J, Raza SA, Brice N, Hausrat TJ, Macharadze T, Diaz-Gonzalez S, Carlton M, Failla AV, Stork O, Schweizer M, Gundelfinger ED, Kneussel M, Spilker C, Karpova A, Kreutz MR. SIPA1L2 controls trafficking and local signaling of trkb-containing amphisomes at presynaptic terminals. Nature Communications. 2019;10:5448. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13224-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreska T, Rauskolb S, Schukraft N, Lüningschrör P, Sasi M, Signoret-Genest J, Behringer M, Blum R, Sauer M, Tovote P, Sendtner M. Induction of BDNF expression in layer II/III and layer V neurons of the motor cortex is essential for motor learning. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2020;40:6289–6308. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0288-20.2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Patterson SL, Alarcon JM, Gromova P, Mata-Roig M, Morozov A, Kandel ER. Gene expression profiling of facilitated L-LTP in VP16-CREB mice reveals that BDNF is critical for the maintenance of LTP and its synaptic capture. Neuron. 2005;48:123–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

