Evaluation of the Abbott Panbio™ COVID-19 antigen detection rapid diagnostic test among healthcare workers in elderly care
- PMID: 36827362
- PMCID: PMC9955641
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276244
Evaluation of the Abbott Panbio™ COVID-19 antigen detection rapid diagnostic test among healthcare workers in elderly care
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been especially dangerous for elderly people. To reduce the risk of transmission from healthcare workers to elderly people, it is of utmost importance to detect possible severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) positive healthcare workers as early as possible. We aimed to determine whether the Abbott Panbio™ COVID-19 antigen detection rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT) could be used as an alternative to reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The second aim was to compare the cycle threshold (Ct) in RT-qPCR with the results of the Ag-RDT.
Methods: A prospective diagnostic evaluation of the Abbott Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag-RDT among healthcare workers across three elderly care facilities as well as home-based elderly care workers who met clinical criteria for COVID-19 during the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Per healthcare worker, the first nasopharyngeal swab was obtained to perform the Ag-RDT and the second swab for RT-qPCR. A Ct-value of < 40 was interpreted as positive, ≥ 40 as negative.
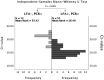
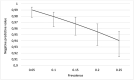
Results: A total of 683 healthcare workers with COVID-19 symptoms were sampled for detection of SARS-CoV-2 by both Ag-RDT and RT-qPCR. Sixty-three healthcare workers (9.2%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-qPCR. The overall sensitivity of Ag-RDT was 81.0% sensitivity (95%CI: 69.6-88.8%) and 100% specificity (95%CI: 99.4-100%). Using a cut-off Ct-value of 32, the sensitivity increased to 92.7% (95% CI: 82.7-97.1%). Negative Ag-RDT results were moderately associated with higher Ct-values (r = 0.62) compared to positive Ag-RDT results.
Conclusion: The Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag-RDT can be used to quickly detect positive SARS-CoV-2 healthcare workers. Negative Ag-RDT should be confirmed by RT-qPCR. In case of severe understaffing and with careful consideration, fully vaccinated healthcare workers with Ag-RDT negative results could work with a mask pending PCR results.
Copyright: © 2023 Eikelenboom-Boskamp et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic evaluation of Panbio™ antigen rapid diagnostic test for SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Virol Methods. 2023 Nov;321:114811. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2023.114811. Epub 2023 Sep 9. J Virol Methods. 2023. PMID: 37696303
-
Diagnostic accuracy of Panbio™ rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 in paediatric population.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Aug 29;23(1):433. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04201-z. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37644389 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of Panbio rapid antigen tests on oropharyngeal swabs for detection of SARS-CoV-2.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 24;16(6):e0253321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253321. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34166410 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative evaluation of RT-PCR and antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) for SARS-CoV-2 detection: performance, variant specificity, and clinical implications.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jun 4;12(6):e0007324. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00073-24. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38683014 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of rapid point-of-care antigen-based diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression analyzing influencing factors.PLoS Med. 2022 May 26;19(5):e1004011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004011. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Med. 2022. PMID: 35617375 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Rapid Antigen Detection Tests and Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses.Int J Public Health. 2023 Aug 1;68:1605452. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1605452. eCollection 2023. Int J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37588042 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Antigen Tests during the COVID-19 Era in Korea and Their Implementation as a Detection Tool for Other Infectious Diseases.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;10(3):322. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10030322. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Contact tracing in the context of COVID-19 (Interim guidance). (2021, February 1). https://www.who.int/.
-
- World Health Organization. Infection prevention and control guidance for long-term care facilities in the context of COVID-19 (Interim guidance). (2020, March 21). https://www.who.int/.
-
- Dutch Association of Elderly Care Physicians. Treatment advice COVID-19 (in Dutch). (2020). www.verenso.nl.
-
- Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Advice antigen (rapid) tests. (2020). https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/documenten/rapporten/2020/10/14/advies-anti....
-
- National Institute for Public Health and the Environment. Guideline COVID-19. (2020) https://lci.rivm.nl/richtlijnen/covid-19.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

