Mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine modulates UCP1 to promote brown adipose thermogenesis
- PMID: 36827367
- PMCID: PMC9956115
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade7864
Mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine modulates UCP1 to promote brown adipose thermogenesis
Abstract
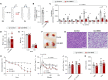
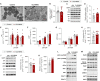
Thermogenesis by uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) is one of the primary mechanisms by which brown adipose tissue (BAT) increases energy expenditure. UCP1 resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), where it dissipates membrane potential independent of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase. Here, we provide evidence that phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) modulates UCP1-dependent proton conductance across the IMM to modulate thermogenesis. Mitochondrial lipidomic analyses revealed PE as a signature molecule whose abundance bidirectionally responds to changes in thermogenic burden. Reduction in mitochondrial PE by deletion of phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (PSD) made mice cold intolerant and insensitive to β3 adrenergic receptor agonist-induced increase in whole-body oxygen consumption. High-resolution respirometry and fluorometry of BAT mitochondria showed that loss of mitochondrial PE specifically lowers UCP1-dependent respiration without compromising electron transfer efficiency or ATP synthesis. These findings were confirmed by a reduction in UCP1 proton current in PE-deficient mitoplasts. Thus, PE performs a previously unknown role as a temperature-responsive rheostat that regulates UCP1-dependent thermogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Hales C. M., Carroll M. D., Fryar C. D., Ogden C. L., Prevalence of prescription pain medication use among adults: United States, 2015–2018. NCHS Data Brief , 1–8 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Schelbert K. B., Comorbidities of obesity. Prim. Care 36, 271–285 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Kopecký J., Hodný Z., Rossmeisl M., Syrový I., Kozak L. P., Reduction of dietary obesity in aP2-Ucp transgenic mice: Physiology and adipose tissue distribution. Am. J. Physiol. 270, E768–E775 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Heden T. D., Johnson J. M., Ferrara P. J., Eshima H., Verkerke A. R. P., Wentzler E. J., Siripoksup P., Narowski T. M., Coleman C. B., Lin C.-T., Ryan T. E., Reidy P. T., de Castro Brás L. E., Karner C. M., Burant C. F., Maschek J. A., Cox J. E., Mashek D. G., Kardon G., Boudina S., Zeczycki T. N., Rutter J., Shaikh S. R., Vance J. E., Drummond M. J., Neufer P. D., Funai K., Mitochondrial PE potentiates respiratory enzymes to amplify skeletal muscle aerobic capacity. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax8352 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cogliati S., Enriquez J. A., Scorrano L., Mitochondrial cristae: Where beauty meets functionality. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 261–273 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK115867/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK130555/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM131854/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK109888/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM144613/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127979/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL165797/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK132239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118333/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK091317/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

