Wellens' syndrome following severe COVID-19 infection, an innocent coincidence or a deadly association: two case reports
- PMID: 36829118
- PMCID: PMC9950701
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03137-7
Wellens' syndrome following severe COVID-19 infection, an innocent coincidence or a deadly association: two case reports
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been associated with late-onset cardiovascular complications primarily due to a hypercoagulable state. Its association with Wellens' syndrome, which reflects a stenosis in the proximal left anterior descending coronary artery, is not well established. We present two cases diagnosed with this syndrome following their COVID-19 acute phase despite taking adequate anticoagulation.
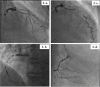
Case presentation: We present two patients with incidental electrocardiography (ECG) showing the typical Wellens'-related changes, with an underlying severe triple-vessel coronary artery disease a few weeks following a severe COVID-19 infection associated with high inflammatory markers. The stenotic lesions were diagnosed by cardiac catheterization, and both patients underwent Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting successfully. Notably, patients' baseline ECGs were normal, and they were maintained on Rivaroxaban 10 mg following their viral illness.
Conclusion: Despite advances in the preventive measures for COVID-19 complications, its pathophysiologic impact on vasculature and atherosclerosis is still incompletely understood. Further clinical trials must be conducted to study this association between Wellens' syndrome and this virus to prevent life-threatening complications.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Atherosclerosis; COVID-19; COVID-19 complications; Wellens’ syndrome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests to report.
Figures


References
-
- Miner B, Grigg WS, Hart EH. Wellens syndrome. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

