Rare mutation-dominant compound EGFR-positive NSCLC is associated with enriched kinase domain-resided variants of uncertain significance and poor clinical outcomes
- PMID: 36829178
- PMCID: PMC9960474
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-02768-z
Rare mutation-dominant compound EGFR-positive NSCLC is associated with enriched kinase domain-resided variants of uncertain significance and poor clinical outcomes
Abstract
Background: Compound epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are less responsive to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) than single EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the detailed clinical characteristics and prognosis of various compound EGFR mutations remain to be elucidated.
Methods: We retrospectively studied the next-generation sequencing (NGS) data of treatment-naïve tumors from 1025 NSCLC patients with compound EGFR mutations, which were sub-categorized into different combinations of common mutations (19-Del and EGFR exon 21 p.L858R), rare mutations, and variants of uncertain significance (VUSs). Prognosis and drug resistance to first-line TKIs were analyzed in 174 and 95 patients, respectively.
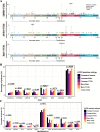
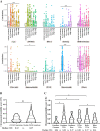
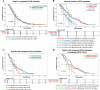
Results: Compound EGFR mutations were enriched with EGFR exon 21 p.L858R and rare mutations, but not 19-Del (P < 0.001). The common + rare and rare + rare subtypes had fewer concurrent mutations in the PI3K pathway (P = 0.032), while the rare + rare and common + VUSs subtypes showed increased association with smoking- and temozolomide-related mutational signatures, respectively (P < 0.001). The rare mutation-dominant subtypes (rare + VUSs and rare + rare) had the worst clinical outcomes to first-line TKIs (P < 0.001), which was further confirmed using an external cohort (P = 0.0066). VUSs in the rare + VUSs subtype selectively reside in the EGFR kinase domain (P < 0.001), implying these tumors might select additional mutations to disrupt the regulation/function of the kinase domain.
Conclusions: Different subtypes of compound EGFR mutations displayed distinct clinical features and genetic architectures, and rare mutation-dominant compound EGFR mutations were associated with enriched kinase domain-resided VUSs and poor clinical outcomes. Our findings help better understand the oncogenesis of compound EGFR mutations and forecast prognostic outcomes of personalized treatments.
Keywords: Compound EGFR mutations; Non-small cell lung cancer; Precision medicine; Resistant mechanism; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
YX, QW, CL, JCY, QO, XW, and YS are employees of Nanjing Geneseeq Technology Inc. All the remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Compound EGFR mutations and response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Jan;8(1):45-51. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182781e35. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23242437 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring different types of EGFR mutations: A retrospective analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Dec;37(6):864-872. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1819-4. Epub 2017 Dec 21. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29270745
-
Non-small cell lung cancer harbouring non-resistant uncommon EGFR mutations: Mutation patterns, effectiveness of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and prognostic factors.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Sep;119:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.06.025. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31425965
-
Heterogeneous Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Uncommon EGFR Mutations: New Insights and Future Perspectives in this Complex Clinical Scenario.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1431. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061431. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The differential prognostic implications of PD-L1 expression in the outcomes of Filipinos with EGFR-mutant NSCLC treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 28;12(9):1896-1911. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-118. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37854154 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation analysis of EGFR mutation detection: Oncomine Dx target test and AmoyDx panel impact on lung cancer treatment decisions.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 18;14(1):1594. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52006-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38238401 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of EGFR mutations subtypes in Moroccan non-small cell lung cancer patients: A first report.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 5;19(6):e0298721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298721. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38837980 Free PMC article.
-
An epidermal growth factor receptor compound mutation of L858R with S768I in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Mar 18;18(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04422-5. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38494473 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics and responses to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR exon 19 insertions.BMC Med. 2025 Apr 29;23(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04075-1. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40301895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, Chitale DA, Dacic S, Giaccone G, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(7):823–859. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318290868f. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

