SGLT-2 inhibitors and in-stent restenosis-related events after acute myocardial infarction: an observational study in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36829203
- PMCID: PMC9960194
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-02781-2
SGLT-2 inhibitors and in-stent restenosis-related events after acute myocardial infarction: an observational study in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: No study evaluated the incidence of intra-stent restenosis (ISR)-related events in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) treated or not with sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i).
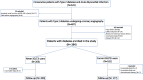
Methods: We recruited 377 patients with T2DM and AMI undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Among them, 177 T2DM were treated with SGLT2 inhibitors before PCI. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as cardiac death, re-infarction, and heart failure related to ISR. In patients without ISR, minimal lumen area and minimal lumen diameter were assessed by coronary CT-angiography at 1-year follow-up.
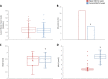
Results: Glycemic control was similar in SGLT2i-treated patients and never SGLT2i-users. The incidence of ISR-related MACE was higher in never SGLT2i-users compared with SGLT2i-treated patients, an effect independent of glycemic status (HR = 0.418, 95% CI = 0.241-0.725, P = 0.002) and observed also in the subgroup of patients with HbA1c < 7% (HR = 0.393, 95% CI = 0.157-0.984, P = 0.027). In patients without the event, the stent patency was greater in SGLT2i-treated patients compared with never SGLT2i-users at 1-year follow-up.
Conclusions: SGLT2i treatment in T2DM is associated with a reduced incidence of ISR-related events, independently of glycemic control.
Keywords: Glycemic control; Major adverse cardiovascular events; Restenosis; SGLT-2 inhibitors; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- JM. Bittl JA, Cohen MG, DiMaio JM, Don CW, Fremes SE, Gaudino MF, Goldberger ZD, Grant MC, Jaswal JB, Kurlansky PA, Mehran R, Metkus TS, Jr, Nnacheta LC, Rao SV, Sellke FW, Sharma G, Yong CM, Zwischenberger BA. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(2):197–215. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.09.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marfella R, Sasso FC, Siniscalchi M, Paolisso P, Rizzo MR, Ferraro F, Stabile E, Sorropago G, Calabrò P, Carbonara O, Cinquegrana G, Piscione F, Ruocco A, D’Andrea D, Rapacciuolo A, Petronella P, Bresciani A, Rubino P, Mauro C, Paolisso G. Peri-procedural tight glycemic control during early percutaneous coronary intervention is associated with a lower rate of in-stent restenosis in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(8):2862–71. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1364. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

