Keep Moving to Retain the Healthy Self: The Influence of Physical Exercise in Health Anxiety among Chinese Menopausal Women
- PMID: 36829369
- PMCID: PMC9952320
- DOI: 10.3390/bs13020140
Keep Moving to Retain the Healthy Self: The Influence of Physical Exercise in Health Anxiety among Chinese Menopausal Women
Abstract
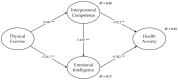
Menopause is a period of high incidence of chronic diseases. Women experience various physical and psychological discomforts during menopause, and hormonal changes exacerbate mood swings in menopausal women and also cause them to begin to experience excessive worry and anxiety about their health problems. This study was a cross-sectional survey investigating the relationship between physical activity and women's health anxiety. Using cluster sampling, a valid sample of 455 females aged 45-50 was collected from 78 communities in five municipal districts in Changsha, China, and AMOS v.23 was adopted to construct a structural equation model to verify the hypotheses. The results indicate that interpersonal competence and emotional intelligence are negatively associated with health anxiety. Furthermore, interpersonal competence and emotional intelligence mediate the relationship between physical exercise and health anxiety, which means that menopausal women with more physical exercise, higher interpersonal competence, and higher emotional intelligence reported lower health anxiety. Finally, to alleviate menopausal women's health anxiety and reduce their risk of chronic diseases, the government, community, and family should create conditions and opportunities for women to participate in group physical activities.
Keywords: emotional intelligence; health anxiety; interpersonal competence; menopausal women; physical exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fostering emotional well-being in adolescents: the role of physical activity, emotional intelligence, and interpersonal forgiveness.Front Psychol. 2024 May 22;15:1408022. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1408022. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38840739 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Links between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity and Self-Rated Health Status in Adolescents: The Mediating Roles of Emotional Intelligence and Psychosocial Stress.Children (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;10(7):1106. doi: 10.3390/children10071106. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508604 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary health approach to quality of life in menopausal women: a community-based interventional study.Clin Interv Aging. 2014 Nov 7;9:1913-21. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S70064. eCollection 2014. Clin Interv Aging. 2014. PMID: 25422589 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ease through menopause with homeopathic and herbal medicine.J Perianesth Nurs. 1999 Jun;14(3):139-43. doi: 10.1016/s1089-9472(99)80007-0. J Perianesth Nurs. 1999. PMID: 10603817 Review.
-
Effects of exogenous melatonin on sleep quality and menopausal symptoms in menopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Menopause. 2021 Mar 26;28(6):717-725. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000001757. Menopause. 2021. PMID: 33784263
Cited by
-
Exploring the Nexus between Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity, Self-Disclosure, Social Anxiety, and Adolescent Social Avoidance: Insights from a Cross-Sectional Study in Central China.Children (Basel). 2023 Dec 30;11(1):56. doi: 10.3390/children11010056. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38255369 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Sustainable Exercise on Self-Efficacy and Life Satisfaction in Women before and after Menopause.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;13(9):759. doi: 10.3390/bs13090759. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754037 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the intake of potentially risky beverages and the occurrence of endometrial polyps: a case-control study.Front Nutr. 2025 Feb 4;12:1538405. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1538405. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39968393 Free PMC article.
-
Influencing Factors of Women's Sports Participation Based on Self-Determination Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024 Aug 8;17:2953-2969. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S465903. eCollection 2024. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2024. PMID: 39136006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of physical exercise on adolescent social anxiety: the serial mediating effects of sports self-efficacy and expressive suppression.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Mar 22;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01107-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40121514 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources