Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System: A Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Sick Leave and Rehabilitation Plan
- PMID: 36829666
- PMCID: PMC9952743
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10020172
Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System: A Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Sick Leave and Rehabilitation Plan
Abstract
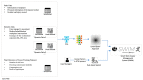
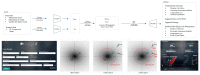
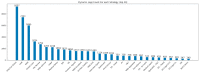
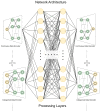
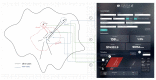
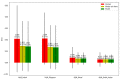
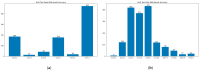
As occupational rehabilitation services are part of the public medical and health services in Hong Kong, work-injured workers are treated along with other patients and are not considered a high priority for occupational rehabilitation services. The idea of a work trial arrangement in the private market occurred to meet the need for a more coordinated occupational rehabilitation practice. However, there is no clear service standard in private occupational rehabilitation services nor concrete suggestions on how to offer rehabilitation plans to injured workers. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) data can provide a foundation for developing a model to improve this situation. This project aims at using a machine-learning-based approach to enhance the traditional prediction of disability duration and rehabilitation plans for work-related injury and illness. To help patients and therapists to understand the machine learning result, we also developed an interactive dashboard to visualize machine learning results. The outcome is promising. Using the variational autoencoder, our system performed better in predicting disability duration. We have around 30% improvement compared with the human prediction error. We also proposed further development to construct a better system to manage the work injury case.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; electronic health record; interactive dashboard; rehabilitation case management; rehabilitation plan; variational autoencoder; work injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System: Artificial Intelligence in Work Disability Management.J Occup Rehabil. 2020 Sep;30(3):354-361. doi: 10.1007/s10926-020-09886-y. J Occup Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 32236811
-
Occupational rehabilitation services provided by a community workers health centre in Hong Kong: a case study.Work. 2008;30(1):5-9. Work. 2008. PMID: 18198433
-
Occupational rehabilitation in Hong Kong: current status and future needs.J Occup Rehabil. 2011 Mar;21 Suppl 1:S28-34. doi: 10.1007/s10926-011-9286-4. J Occup Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21274739
-
Intelligent Robotics Incorporating Machine Learning Algorithms for Improving Functional Capacity Evaluation and Occupational Rehabilitation.J Occup Rehabil. 2020 Sep;30(3):362-370. doi: 10.1007/s10926-020-09888-w. J Occup Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 32253595 Review.
-
A review on utilizing machine learning technology in the fields of electronic emergency triage and patient priority systems in telemedicine: Coherent taxonomy, motivations, open research challenges and recommendations for intelligent future work.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Sep;209:106357. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106357. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34438223 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Data Mining and Visualization of Sensory-Graph-Modeled Datasets through Summarization.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 14;24(14):4554. doi: 10.3390/s24144554. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065952 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic Health Records for Predicting Outcomes to Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Scoping Review.J Occup Rehabil. 2024 Dec;34(4):770-782. doi: 10.1007/s10926-024-10175-1. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Occup Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38536622 Free PMC article.
-
The PDC30 Chatbot-Development of a Psychoeducational Resource on Dementia Caregiving Among Family Caregivers: Mixed Methods Acceptability Study.JMIR Aging. 2025 Jan 6;8:e63715. doi: 10.2196/63715. JMIR Aging. 2025. PMID: 39761547 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Accuracy of the Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System to Assist Case Managers in Predicting the Work Disability of Injured Workers.J Occup Rehabil. 2025 Jun;35(2):320-332. doi: 10.1007/s10926-024-10199-7. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Occup Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 38874680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu S., Vahedian F., Hachen D., Lizardo O., Poellabauer C., Striegel A., Milenković T. Heterogeneous Network Approach to Predict Individuals’ Mental Health. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data. 2021;15:1–26. doi: 10.1145/3429446. - DOI
-
- Wang Y., Chen W., Pi D., Yue L. Adversarially regularized medication recommendation model with multi-hop memory network. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2021;63:125–142. doi: 10.1007/s10115-020-01513-9. - DOI
-
- Yao L., Zhang Y., Wei B., Zhang W., Jin Z. A Topic Modeling Approach for Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescriptions. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (TKDE) 2018;30:1007–1021. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2787158. - DOI
-
- Spiotta M., Terenziani P., Dupré D.T. Temporal Conformance Analysis and Explanation of Clinical Guidelines Execution: An Answer Set Programming Approach. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017;29:2567–2580. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2734084. - DOI
-
- Solares J.R., Raimondi F.E., Zhu Y., Rahimian F., Canoy D., Tran J., Gomes A.C., Payberah A.H., Zottoli M., Nazarzadeh M., et al. Deep learning for electronic health records: A comparative review of multiple deep neural architectures. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020;101:103337. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103337. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

