Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System: A Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Sick Leave and Rehabilitation Plan
- PMID: 36829666
- PMCID: PMC9952743
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10020172
Smart Work Injury Management (SWIM) System: A Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Sick Leave and Rehabilitation Plan
Abstract
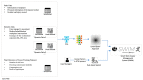
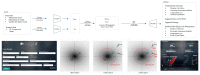
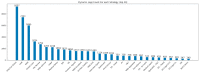
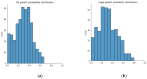
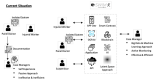
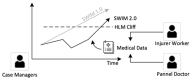
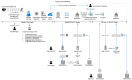
As occupational rehabilitation services are part of the public medical and health services in Hong Kong, work-injured workers are treated along with other patients and are not considered a high priority for occupational rehabilitation services. The idea of a work trial arrangement in the private market occurred to meet the need for a more coordinated occupational rehabilitation practice. However, there is no clear service standard in private occupational rehabilitation services nor concrete suggestions on how to offer rehabilitation plans to injured workers. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) data can provide a foundation for developing a model to improve this situation. This project aims at using a machine-learning-based approach to enhance the traditional prediction of disability duration and rehabilitation plans for work-related injury and illness. To help patients and therapists to understand the machine learning result, we also developed an interactive dashboard to visualize machine learning results. The outcome is promising. Using the variational autoencoder, our system performed better in predicting disability duration. We have around 30% improvement compared with the human prediction error. We also proposed further development to construct a better system to manage the work injury case.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; electronic health record; interactive dashboard; rehabilitation case management; rehabilitation plan; variational autoencoder; work injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu S., Vahedian F., Hachen D., Lizardo O., Poellabauer C., Striegel A., Milenković T. Heterogeneous Network Approach to Predict Individuals’ Mental Health. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data. 2021;15:1–26. doi: 10.1145/3429446. - DOI
-
- Wang Y., Chen W., Pi D., Yue L. Adversarially regularized medication recommendation model with multi-hop memory network. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2021;63:125–142. doi: 10.1007/s10115-020-01513-9. - DOI
-
- Yao L., Zhang Y., Wei B., Zhang W., Jin Z. A Topic Modeling Approach for Traditional Chinese Medicine Prescriptions. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (TKDE) 2018;30:1007–1021. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2787158. - DOI
-
- Spiotta M., Terenziani P., Dupré D.T. Temporal Conformance Analysis and Explanation of Clinical Guidelines Execution: An Answer Set Programming Approach. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017;29:2567–2580. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2734084. - DOI
-
- Solares J.R., Raimondi F.E., Zhu Y., Rahimian F., Canoy D., Tran J., Gomes A.C., Payberah A.H., Zottoli M., Nazarzadeh M., et al. Deep learning for electronic health records: A comparative review of multiple deep neural architectures. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020;101:103337. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103337. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

