Ether Lipid-Mediated Antioxidant Defense in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 36829852
- PMCID: PMC9952080
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12020293
Ether Lipid-Mediated Antioxidant Defense in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
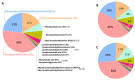
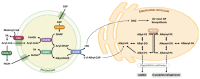
One of the richest tissues in lipid content and diversity of the human body is the brain. The human brain is constitutively highly vulnerable to oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is a determinant in brain aging, as well as in the onset and progression of sporadic (late-onset) Alzheimer's disease (sAD). Glycerophospholipids are the main lipid category widely distributed in neural cell membranes, with a very significant presence for the ether lipid subclass. Ether lipids have played a key role in the evolution of the human brain compositional specificity and functionality. Ether lipids determine the neural membrane structural and functional properties, membrane trafficking, cell signaling and antioxidant defense mechanisms. Here, we explore the idea that ether lipids actively participate in the pathogenesis of sAD. Firstly, we evaluate the quantitative relevance of ether lipids in the human brain composition, as well as their role in the human brain evolution. Then, we analyze the implications of ether lipids in neural cell physiology, highlighting their inherent antioxidant properties. Finally, we discuss changes in ether lipid content associated with sAD and their physiopathological implications, and propose a mechanism that, as a vicious cycle, explains the potential significance of ether lipids in sAD.
Keywords: antioxidants; human brain; lipid oxidation; lipidomics; neurodegeneration; plasmalogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Thudichum J.L. A Treatise on the Chemical Constitution of the Brain. Archon Books; Hamden, CT, USA: 1962.
-
- Bozek K., Wei Y., Yan Z., Liu X., Xiong J., Sugimoto M., Tomita M., Pääbo S., Sherwood C.C., Hof P.R., et al. Organization and Evolution of Brain Lipidome Revealed by Large-Scale Analysis of Human, Chimpanzee, Macaque, and Mouse Tissues. Neuron. 2015;85:695–702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- PP10605 - PIRS2021/Diputació de Lleida
- RTI2018-099200-B-I00/Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities
- SLT002/16/00250/Generalitat of Catalonia: Department of Health
- 2021SGR00990/Generalitat of Catalonia: Agency for Management of University and Research Grants
- PI19/00155/Institute of Health Carlos III

