Pleiotropic Roles of a KEAP1-Associated Deubiquitinase, OTUD1
- PMID: 36829909
- PMCID: PMC9952104
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12020350
Pleiotropic Roles of a KEAP1-Associated Deubiquitinase, OTUD1
Abstract
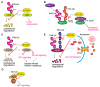
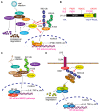
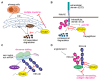
Protein ubiquitination, which is catalyzed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and ubiquitin ligases, is a crucial post-translational modification to regulate numerous cellular functions in a spatio-temporal-specific manner. The human genome encodes ~100 deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), which antagonistically regulate the ubiquitin system. OTUD1, an ovarian tumor protease (OTU) family DUB, has an N-terminal-disordered alanine-, proline-, glycine-rich region (APGR), a catalytic OTU domain, and a ubiquitin-interacting motif (UIM). OTUD1 preferentially hydrolyzes lysine-63-linked ubiquitin chains in vitro; however, recent studies indicate that OTUD1 cleaves various ubiquitin linkages, and is involved in the regulation of multiple cellular functions. Thus, OTUD1 predominantly functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting p53, SMAD7, PTEN, AKT, IREB2, YAP, MCL1, and AIF. Furthermore, OTUD1 regulates antiviral signaling, innate and acquired immune responses, and cell death pathways. Similar to Nrf2, OTUD1 contains a KEAP1-binding ETGE motif in its APGR and regulates the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress response and cell death. Importantly, in addition to its association with various cancers, including multiple myeloma, OTUD1 is involved in acute graft-versus-host disease and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. Thus, OTUD1 is an important DUB as a therapeutic target for a variety of diseases.
Keywords: KEAP1; OTUD1; antiviral response; cancer; cell death; deubiquitinating enzyme; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

