Antenatal and Postnatal Sequelae of Oxidative Stress in Preterm Infants: A Narrative Review Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms
- PMID: 36829980
- PMCID: PMC9952227
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12020422
Antenatal and Postnatal Sequelae of Oxidative Stress in Preterm Infants: A Narrative Review Targeting Pathophysiological Mechanisms
Abstract
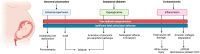
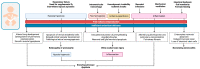
The detrimental effects of oxidative stress (OS) can start as early as after conception. A growing body of evidence has shown the pivotal role of OS in the development of several pathological conditions during the neonatal period, which have been therefore defined as OS-related neonatal diseases. Due to the physiological immaturity of their antioxidant defenses and to the enhanced antenatal and postnatal exposure to free radicals, preterm infants are particularly susceptible to oxidative damage, and several pathophysiological cascades involved in the development of prematurity-related complications are tightly related to OS. This narrative review aims to provide a detailed overview of the OS-related pathophysiological mechanisms that contribute to the main OS-related diseases during pregnancy and in the early postnatal period in the preterm population. Particularly, focus has been placed on pregnancy disorders typically associated with iatrogenic or spontaneous preterm birth, such as intrauterine growth restriction, pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, chorioamnionitis, and on specific postnatal complications for which the role of OS has been largely ascertained (e.g., respiratory distress, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, retinopathy of prematurity, periventricular leukomalacia, necrotizing enterocolitis, neonatal sepsis). Knowledge of the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms may increase awareness on potential strategies aimed at preventing the development of these conditions or at reducing the ensuing clinical burden.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; chorioamnionitis; gestational diabetes; necrotizing enterocolitis; oxidative stress; pre-eclampsia; preterm birth; retinopathy of prematurity; sepsis; white matter injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

