Antioxidant Protection against Trastuzumab Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 36830015
- PMCID: PMC9952697
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12020457
Antioxidant Protection against Trastuzumab Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer Therapy
Abstract
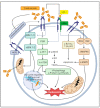
Breast cancer is the most frequent malignant neoplastic disease in women, with an estimated 2.3 million cases in 2020 worldwide. Its treatment depends on characteristics of the patient and the tumor. In the latter, characteristics include cell type and morphology, anatomical location, and immunophenotype. Concerning this latter aspect, the overexpression of the HER2 receptor, expressed in 15-25% of tumors, is associated with greater aggressiveness and worse prognosis. In recent times some monoclonal antibodies have been developed in order to target HER2 receptor overexpression. Trastuzumab is part of the monoclonal antibodies used as targeted therapy against HER2 receptor, whose major problem is its cardiac safety profile, where it has been associated with cardiotoxicity. The appearance of cardiotoxicity is an indication to stop therapy. Although the pathophysiological mechanism is poorly known, evidence indicates that oxidative stress plays a fundamental role causing DNA damage, increased cytosolic and mitochondrial ROS production, changes in mitochondrial membrane potential, intracellular calcium dysregulation, and the consequent cell death through different pathways. The aim of this review was to explore the use of antioxidants as adjuvant therapy to trastuzumab to prevent its cardiac toxicity, thus leading to ameliorate its safety profile in its administration.
Keywords: antioxidants; cardiotoxicity; immunotherapy; oxidative stress; trastuzumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2019. [(accessed on 25 December 2022)]. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/gho-documents/global-healt....
-
- World Health Organization Breast Cancer. [(accessed on 25 December 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

