Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 36830075
- PMCID: PMC9952099
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12020517
Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
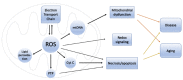
Neurodegenerative disorders constitute a substantial proportion of neurological diseases with significant public health importance. The pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases is characterized by a complex interplay of various general and disease-specific factors that lead to the end point of neuronal degeneration and loss, and the eventual clinical manifestations. Oxidative stress is the result of an imbalance between pro-oxidant species and antioxidant systems, characterized by an elevation in the levels of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species, and a reduction in the levels of endogenous antioxidants. Recent studies have increasingly highlighted oxidative stress and associated mitochondrial dysfunction to be important players in the pathophysiologic processes involved in neurodegenerative conditions. In this article, we review the current knowledge of the general effects of oxidative stress on the central nervous system, the different specific routes by which oxidative stress influences the pathophysiologic processes involved in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Huntington's disease, and how oxidative stress may be therapeutically reversed/mitigated in order to stall the pathological progression of these neurodegenerative disorders to bring about clinical benefits.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; free radicals; homeostasis; mitochondrial stress; reactive nitrogen species; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

