Host Dependent-Transposon for a Plasmid Found in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida That Bears a catB3 Gene for Chloramphenicol Resistance
- PMID: 36830168
- PMCID: PMC9952659
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12020257
Host Dependent-Transposon for a Plasmid Found in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida That Bears a catB3 Gene for Chloramphenicol Resistance
Abstract
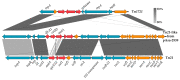
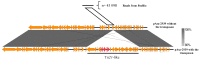
Plasmids that carry antibiotic resistance genes occur frequently in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, an aquatic pathogen with severe consequences in salmonid farming. Here, we describe a 67 kb plasmid found in the A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida Strain SHY15-2939 from Quebec, Canada. This new plasmid, named pAsa-2939 and identified by high throughput sequencing, displays features never found before in this bacterial species. It contains a transposon related to the Tn21 family, but with an unusual organization. This transposon bears a catB3 gene (chloramphenicol resistance) that has not been detected yet in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. The plasmid is transferable by conjugation into Aeromonas hydrophila, but not into Escherichia coli. Based on PCR analysis and genomic sequencing (Illumina and PacBio), we determined that the transposon is unstable in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida Strain SHY15-2939, but it is stable in A. hydrophila trans-conjugants, which explains the chloramphenicol resistance variability observed in SHY15-2939. These results suggest that this bacterium is likely not the most appropriate host for this plasmid. The presence of pAsa-2939 in A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida also strengthens the reservoir role of this bacterium for antibiotic resistance genes, even those that resist antibiotics not used in aquaculture in Québec, such as chloramphenicol.
Keywords: Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida; antibiotic resistance gene; chloramphenicol; pAsa-2939; plasmid; transposon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449: insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen.BMC Genomics. 2008 Sep 18;9:427. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-427. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18801193 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic resistance due to an unusual ColE1-type replicon plasmid in Aeromonas salmonicida.Microbiology (Reading). 2016 Jun;162(6):942-953. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000286. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Microbiology (Reading). 2016. PMID: 27028891
-
One Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida isolate with a pAsa5 variant bearing antibiotic resistance and a pRAS3 variant making a link with a swine pathogen.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Nov 10;690:313-320. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.456. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 31299566
-
Virulence, genomic features, and plasticity of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, the causative agent of fish furunculosis.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Feb 21;169(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 23890675 Review.
-
The Aeromonas salmonicida plasmidome: a model of modular evolution and genetic diversity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021 Mar;1488(1):16-32. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14503. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021. PMID: 33040386 Review.
Cited by
-
Aeromonas trota Is Highly Refractory to Acquire Exogenous Genetic Material.Microorganisms. 2024 May 28;12(6):1091. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061091. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930473 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, Identification, and Characteristics of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. masoucida from Diseased Starry Flounder (Platichthys stellatus).Pathogens. 2025 Mar 5;14(3):257. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030257. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40137743 Free PMC article.
-
Co-purification of the GroEL chaperone during outer membrane vesicle purification: insights from Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida.Microbiology (Reading). 2025 Apr;171(4):001558. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001558. Microbiology (Reading). 2025. PMID: 40293439 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of pAsa5 and pAsa8 Plasmids in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 2;11(11):2685. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112685. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004697 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Pangenomic Insights into Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. oncorhynchi subsp. nov.Pathogens. 2025 May 23;14(6):523. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14060523. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40559531 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austin B., Austin D.A. Aeromonadaceae Representative (Aeromonas salmonicida). In Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish; Austin, B., Austin, D.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing; New York; NY; USA: 2016; pp. 215–321
-
- Reith M.E., Singh R.K., Curtis B., Boyd J.M., Bouevitch A., Kimball J., Munholland J., Murphy C., Sarty D., Williams J., et al. The genome of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida A449: Insights into the evolution of a fish pathogen. BMC Genom. 2008;9:427. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

