Evaluation of Antiproliferative, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Phytochemical Analysis of Anogeissus dhofarica A. J. Scott
- PMID: 36830265
- PMCID: PMC9952305
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12020354
Evaluation of Antiproliferative, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Antidiabetic and Phytochemical Analysis of Anogeissus dhofarica A. J. Scott
Abstract
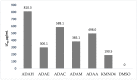
In the current study, methanol (ADAM) extracts and their fractions, including chloroform (ADAC), ethyl acetate (ADAE), n-hexane (ADAH), and aqueous (ADAA) fractions, were prepared from aerial parts of Anogeissus dhofarica and evaluated for phytochemical assessment, high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS) analysis, and in vitro bioassays. The qualitative analysis determined that, except alkaloids, all the representative groups were found to be present in the analyzed samples. Samples under quantitative study displayed the highest amount of total phenolic contents in the ADAE fraction, while total flavonoid contents were highest in the ADAM extract. The ADAM extract was subjected to HR-ESI-MS to identify the chemical constituents that presented twenty-two bioactive ingredients, outlined for the first time from A. dhofarica, mainly contributed by sub-class flavanones. In the case of antimicrobial activity, the ADAE extract revealed an effective zone of inhibition (ZOI) against the Gram-positive bacterial strain (Staphylococcus aureus) with an MIC value of 0.78 ± 0.3 mg/mL, while the ADAA extract exhibited higher ZOI (34 ± 0.12 mm) against the fungal strain Candida kruzei with an MIC of 0.78 mg/mL. In the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) analysis, the ADAE extract exhibited a maximum scavenging potential with an IC50 of 9.8 ± 1.2 μg/mL, succeeded by the ADAM extract with an IC50 of 17.4 ± 0.4 μg/mL free radical scavenging capability. In the antidiabetic assessment, the ADAE extract was the most effective, with an IC50 of 6.40 ± 0.1 μg/mL, while the same extract demonstrated prominent activity with 30.8% viability and an IC50 of 6.2 ± 0.3 μg/mL against breast cancer cell lines. The brine shrimp lethality assay demonstrated a correlation with the in vitro cytotoxicity assay, showing the ADAE extract as the most active, with a 70% mortality rate and an LC50 of 300.1 μg/mL. In conclusion, all the tested samples, especially the ADAE and ADAM extracts, have significant capabilities for the investigated activities that could be due to the presence of the bioactive compounds.
Keywords: Anogeissus dhofarica A. J. Scott; HR-ESI-MS; antidiabetic; antimicrobial; antioxidant; cytotoxicity; phytochemical analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Scutellaria petiolata Hemsl. ex Lace & Prain (Lamiaceae).: A New Insight in Biomedical Therapies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1446. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081446. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892648 Free PMC article.
-
Polarity directed optimization of phytochemical and in vitro biological potential of an indigenous folklore: Quercus dilatata Lindl. ex Royle.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Aug 3;17(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1894-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28774308 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Silybum marianum L. seeds from Pakistan for its antibacterial, antioxidant, antidiabetic activities, and phytochemical analysis.Nat Prod Res. 2025 Mar 13:1-7. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2025.2475506. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 40079064
-
Phytochemical Analysis of Centaurea calcitrapa L. Aerial Flowering Parts Serial Solvent Extracts and Its Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;14(7):900. doi: 10.3390/life14070900. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39063653 Free PMC article.
-
Appraisal of phytochemical and in vitro biological attributes of an unexplored folklore: Rhus Punjabensis Stewart.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Mar 9;17(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1659-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28274230 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Eriocitrin Disrupts Erythrocyte Membrane Asymmetry through Oxidative Stress and Calcium Signaling and the Activation of Casein Kinase 1α and Rac1 GTPase.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 2;16(12):1681. doi: 10.3390/ph16121681. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38139808 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling and Bioactivity of Polyphenols from the Omani Medicinal Plant Terminalia dhofarica (syn. Anogeissus dhofarica).Molecules. 2025 Feb 18;30(4):952. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040952. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raina H., Soni G., Jauhari N., Sharma N., Bharadvaja N. Phytochemical importance of medicinal plants as potential sources of anticancer agents. Turk. J. Bot. 2014;38:1027–1035. doi: 10.3906/bot-1405-93. - DOI
-
- Mohammed A.H. Importance of medicinal plants. Res. Pharm. Health Sci. 2019;5:124–125. doi: 10.32463/rphs.2019.v05i02.01. - DOI
-
- Muhammad Z., Nasir R., Asim M., Fozia A., Munawar I., Muhammad M., Muhammad S. Antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal activities and phytochemical analysis of dagger (Yucca aloifolia) leaves extracts. J. Med. Plants Res. 2013;7:243–249.
-
- Ur Rehman F., Kalsoom M., Adnan M., Fazeli-Nasab B., Naz N., Ilahi H., Ali M.F., Ilyas M., Yousaf G., Toor M.D. Importance of medicinal plants in human and plant pathology: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Biomed. Res. 2021;8:1–11. doi: 10.18782/2394-3726.1110. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

