Particle Nanoarchitectonics for Nanomedicine and Nanotherapeutic Drugs with Special Emphasis on Nasal Drugs and Aging
- PMID: 36830891
- PMCID: PMC9953552
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11020354
Particle Nanoarchitectonics for Nanomedicine and Nanotherapeutic Drugs with Special Emphasis on Nasal Drugs and Aging
Abstract
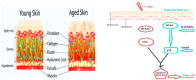
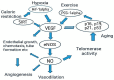
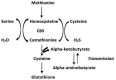
Aging is a multifunctional physiological manifestation. The nasal cavity is considered a major site for easy and cost-effective drug and vaccine administration, due to high permeability, low enzymatic activity, and the presence of a high number of immunocompetent cells. This review article primarily focuses on aging genetics, physical parameters, and the use of nanoparticles as delivery systems of drugs and vaccines via the nasal cavity. Studies have identified various genes involved in centenarian and average-aged people. VEGF is a key mediator involved in angiogenesis. Different therapeutic approaches induce vascular function and angiogenesis. FOLR1 gene codes for folate receptor alpha protein that helps in regulating the transport of vitamin B folate, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs inside the cell. This gene also aids in slowing the aging process down by cellular regeneration and promotes healthy aging by reducing aging symptoms. It has been found through the literature that GATA 6, Yamanaka factors, and FOLR1 work in synchronization to induce healthy and delayed aging. The role and applications of genes including CBS, CISD, SIRT 1, and SIRT 6 play a significant role in aging.
Keywords: FOLR1; GATA6; NALT; angiogenesis; nanotherapeutics; nasal drugs; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of antiepileptic drugs and reactive oxygen species on folate receptor 1 (FOLR1)-dependent 5-methyltetrahydrofolate transport.Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Sep;101(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.05.006. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Mol Genet Metab. 2010. PMID: 20619709
-
CIC de novo loss of function variants contribute to cerebral folate deficiency by downregulating FOLR1 expression.J Med Genet. 2021 Jul;58(7):484-494. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-106987. Epub 2020 Aug 20. J Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 32820034 Free PMC article.
-
Folate and Pegylated Aliphatic Polyester Nanoparticles for Targeted Anticancer Drug Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jul 10;15:4899-4918. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S244712. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32764924 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticulate systems for nasal delivery of drugs: a real improvement over simple systems?J Pharm Sci. 2007 Mar;96(3):473-83. doi: 10.1002/jps.20718. J Pharm Sci. 2007. PMID: 17117404 Review.
-
Potential of nanoparticulate drug delivery systems by intranasal administration.Curr Pharm Des. 2010 May;16(14):1644-53. doi: 10.2174/138161210791164108. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20210751 Review.
Cited by
-
Immobilization of Aspergillus oryzae tyrosine hydroxylase on ZnO nanocrystals for improved stability and catalytic efficiency towards L-dopa production.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 18;13(1):22882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50198-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38129644 Free PMC article.
-
Phyto-Assisted Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) Using Delonix elata Extract: Characterization, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Photocatalytic Activities.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01449-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40490606
-
Targeted Gene Delivery to MCF-7 Cells via Polyspermine-PEG-Glucose/DNA Nanoparticles: Preparation and Characterization.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 5. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01454-0. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40473897
-
Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles from Madhuca indica Plant Extract and Assessment of Their Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Diabetic Properties via Different Nanoinformatics Approaches.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 7;8(37):33358-33366. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02744. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37744851 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Natural Compounds as Potential CDK4 Inhibitors for Therapeutic Intervention in Neurodegenerative Diseases through Computational Analysis.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;67(8):3310-3329. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01258-8. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39207668
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

