Electric Fields Regulate In Vitro Surface Phosphatidylserine Exposure of Cancer Cells via a Calcium-Dependent Pathway
- PMID: 36831002
- PMCID: PMC9953458
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11020466
Electric Fields Regulate In Vitro Surface Phosphatidylserine Exposure of Cancer Cells via a Calcium-Dependent Pathway
Abstract
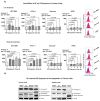
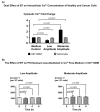
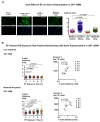
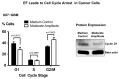
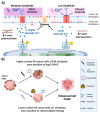
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide after heart disease. The current treatment options to fight cancer are limited, and there is a critical need for better treatment strategies. During the last several decades, several electric field (EF)-based approaches for anti-cancer therapies have been introduced, such as electroporation and tumor-treating fields; still, they are far from optimal due to their invasive nature, limited efficacy and significant side effects. In this study, we developed a non-contact EF stimulation system to investigate the in vitro effects of a novel EF modality on cancer biomarkers in normal (human astrocytes, human pancreatic ductal epithelial -HDPE-cells) and cancer cell lines (glioblastoma U87-GBM, human pancreatic cancer cfPac-1, and MiaPaCa-2). Our results demonstrate that this EF modality can successfully modulate an important cancer cell biomarker-cell surface phosphatidylserine (PS). Our results further suggest that moderate, but not low, amplitude EF induces p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), actin polymerization, and cell cycle arrest in cancer cell lines. Based on our results, we propose a mechanism for EF-mediated PS exposure in cancer cells, where the magnitude of induced EF on the cell surface can differentially regulate intracellular calcium (Ca2+) levels, thereby modulating surface PS exposure.
Keywords: calcium modulation; cancer biomarker; electric field; enhanced cancer therapy; p38 MAPK-actin pathway; surface phosphatidylserine exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Russano F., Del Fiore P., Di Prata C., Pasqual A., Marconato R., Campana L.G., Spina R., Gianesini C.M., Collodetto A., Tropea S., et al. The Role of Electrochemotherapy in the Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Metastases From Breast Cancer: Analysis of Predictive Factors to Treatment From an Italian Cohort of Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:772144. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.772144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sieni E., Dettin M., De Robertis M., Bazzolo B., Conconi M.T., Zamuner A., Marino R., Keller F., Campana L.G., Signori E. The Efficiency of Gene Electrotransfer in Breast-Cancer Cell Lines Cultured on a Novel Collagen-Free 3D Scaffold. Cancers. 2020;12:1043. doi: 10.3390/cancers12041043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

