Diagnosis and Assessment of Dental Caries Using Novel Bioactive Caries Detecting Dye Solution
- PMID: 36831036
- PMCID: PMC9953294
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11020500
Diagnosis and Assessment of Dental Caries Using Novel Bioactive Caries Detecting Dye Solution
Abstract
Background: The goal of materials should be early caries detection, removal of carious lesions, and reduction of dentin hypersensitivity. Thus, the study aims to determine the efficacy of a bioactive caries detecting dye (BCD) for the diagnosing and mechanical removal of occlusal and proximal dental caries.
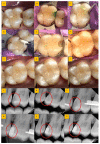
Methods: Patients with occlusal (A1, A2) and proximal carious lesions (B1, B2) were treated with the rotary technique and BCD solution on 120 teeth (n = 60 for each). Group 1: Excavation was performed using diamond points. Group 2: 0.5 mL of BCD solution was scrubbed for 20 sec and excavation was performed with a sharp spoon excavator. Post-excavation cavity volume analysis was performed using a 3D scanner. The time required, VAS for pain, VAS for facial expression, and sound eye motor scoring were scored during excavation. Post-restoration evaluation was performed at 3, 6, and 12 months (FDI criteria).
Results: The chi-square test revealed that the A1 (197.90 30.97 s) and B1 (273.06 69.95 s) had significantly less mean procedural time than the A2 (292.13 44.87 s) and B2 (411.86 88.34 s). BCD (A2, B2) group showed good patient acceptance, less pain during caries excavation VAS (p = 0.001, FACE (p = 0.001), and SEM (p < 0.001) analysis than the rotary group. There was a statistically insignificant difference between groups immediately (p = 0.235), (p = 0.475) and after 24 h (p = 0.561), (p = 0.688). Color score, hardness of excavated surface, and caries removal score for occlusal and proximal groups showed insignificant differences between the groups. BCD group showed significantly less mean caries excavated volume for the occlusal group (p = 0.003) as compared to the proximal group (p = 0.417) evaluated by 3D scanner. Evaluation of restoration after 3-, 6-, and 12 months intervals (Occlusal caries group (p = 0.247), (p = 0.330), and (0.489) and Proximal caries group (p = 0.299), (p = 0.594), and (0.494)) was acceptable for both the groups.
Conclusion: BCD helps in identification of dental caries clinically, radiographically, and in effective removal of denatured teeth with less pain or sensitivity.
Keywords: 3D scanner; bioactive caries detecting dye solution; caries excavation; chemomechanical caries removal; dental caries; dentin hypersensitivity; diagnostic imaging; minimal intervention dentistry; pain perception.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Volumetric analysis after caries excavation with caries detecting dyes and chemomechanical caries removal agents using 3D scanner-a randomised clinical trial.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Feb 1;24(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03907-5. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38302932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analyzing working time and efficient caries removal using a novel bioactive caries detecting dye and air polisher prophy for caries excavation: randomised clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Mar 15;28(4):214. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05609-2. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38485869 Clinical Trial.
-
Novel bioactive caries-detecting dye solution: Cytotoxicity, antimicrobial activity, scanning electron microscope, and stereomicroscopic analysis in diagnosis of dental caries.J Conserv Dent. 2020 Jan-Feb;23(1):79-85. doi: 10.4103/JCD.JCD_154_20. Epub 2020 Oct 10. J Conserv Dent. 2020. PMID: 33223647 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Different Caries Excavation Techniques in reducing the Cariogenic Flora: An in vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016 Jul-Sep;9(3):214-217. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1366. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016. PMID: 27843252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials on Chemomechanical Caries Removal.Oper Dent. 2015 Jul-Aug;40(4):E167-78. doi: 10.2341/14-021-LIT. Oper Dent. 2015. PMID: 26167737
Cited by
-
Caries Lesion Assessment Using 3D Virtual Models by Examiners with Different Degrees of Clinical Experience.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 13;59(12):2157. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122157. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138260 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate Patient Satisfaction with Dental Esthetics After Endodontic and Prosthodontic Treatment of Dental Dyschromia.Dent J (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;13(1):44. doi: 10.3390/dj13010044. Dent J (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39851620 Free PMC article.
-
The Penetration Depth of Resin Infiltration Into Enamel: A Systematic Review.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023 Jun 29;13(3):194-207. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_36_23. eCollection 2023 May-Jun. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023. PMID: 37564169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Volumetric analysis after caries excavation with caries detecting dyes and chemomechanical caries removal agents using 3D scanner-a randomised clinical trial.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Feb 1;24(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-03907-5. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38302932 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Analyzing working time and efficient caries removal using a novel bioactive caries detecting dye and air polisher prophy for caries excavation: randomised clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Mar 15;28(4):214. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05609-2. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38485869 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Najibfard K., Ramalingam K., Chedjieu I., Amaechi B.T. Remineralization of Early Caries by a Nano-Hydroxyapatite Dentifrice. J. Clin. Dent. 2011;22:139. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg M. Enamel and Dentin Carious Lesions. JSM Dent. 2020;8:1120.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

