Wnt Pathway in Pancreatic Development and Pathophysiology
- PMID: 36831232
- PMCID: PMC9954665
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12040565
Wnt Pathway in Pancreatic Development and Pathophysiology
Abstract
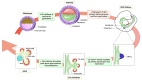
The pancreas is an abdominal gland that serves 2 vital purposes: assist food processing by secreting digestive enzymes and regulate blood glucose levels by releasing endocrine hormones. During embryonic development, this gland originates from epithelial buds located on opposite sites of the foregut endoderm. Pancreatic cell specification and maturation are coordinated by a complex interplay of extrinsic and intrinsic signaling events. In the recent years, the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway has emerged as an important player of pancreas organogenesis, regulating pancreatic epithelium specification, compartmentalization and expansion. Importantly, it has been suggested to regulate proliferation, survival and function of adult pancreatic cells, including insulin-secreting β-cells. This review summarizes recent work on the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in pancreas biology from early development to adulthood, emphasizing on its relevance for the development of new therapies for pancreatic diseases.
Keywords: Wnt pathway; diabetes; embryonic development; pancreas; β-catenin; β-cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Patrick Collombat is scientific consultant at DiogenX. Tiziana Napolitano, Serena Silvano, Magali Plaisant and Benjamin Charles are employed by DiogenX.
Figures


References
-
- Pandol S. The Exocrine Pancreas. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences; San Rafael, CA, USA: 2010. Water and ion secretion from the pancreatic ductal system. - PubMed
-
- Courtney M., Pfeifer A., Al-Hasani K., Gjernes E., Vieira A., Ben-Othman N., Collombat P. In vivo conversion of adult alpha-cells into beta-like cells: A new research avenue in the context of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011;13((Suppl. S1)):47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01441.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

