MAPK Pathways in Ocular Pathophysiology: Potential Therapeutic Drugs and Challenges
- PMID: 36831285
- PMCID: PMC9954064
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12040617
MAPK Pathways in Ocular Pathophysiology: Potential Therapeutic Drugs and Challenges
Abstract
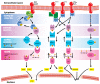
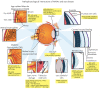
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways represent ubiquitous cellular signal transduction pathways that regulate all aspects of life and are frequently altered in disease. Once activated through phosphorylation, these MAPKs in turn phosphorylate and activate transcription factors present either in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus, leading to the expression of target genes and, as a consequence, they elicit various biological responses. The aim of this work is to provide a comprehensive review focusing on the roles of MAPK signaling pathways in ocular pathophysiology and the potential to influence these for the treatment of eye diseases. We summarize the current knowledge of identified MAPK-targeting compounds in the context of ocular diseases such as macular degeneration, cataract, glaucoma and keratopathy, but also in rare ocular diseases where the cell differentiation, proliferation or migration are defective. Potential therapeutic interventions are also discussed. Additionally, we discuss challenges in overcoming the reported eye toxicity of some MAPK inhibitors.
Keywords: ERK; JNK; MAPK; eye toxicity; ocular diseases; p38; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
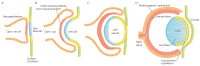
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

