Toxicity of Asciminib in Real Clinical Practice: Analysis of Side Effects and Cross-Toxicity with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 36831388
- PMCID: PMC9954054
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15041045
Toxicity of Asciminib in Real Clinical Practice: Analysis of Side Effects and Cross-Toxicity with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
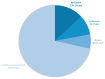
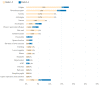
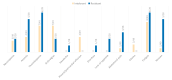
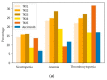
(1) Background: Despite the prognostic improvements achieved with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a minority of patients still fail TKIs. The recent introduction of asciminib may be a promising option in intolerant patients, as it is a first-in-class inhibitor with a more selective mechanism of action different from the ATP-competitive inhibition that occurs with TKIs. Therefore, our goal was to analyze toxicities shown with asciminib as well as to study cross-toxicity with previous TKIs. (2) Methods: An observational, multicenter, retrospective study was performed with data from 77 patients with CML with therapeutic failure to second-generation TKIs who received asciminib through a managed-access program (MAP) (3) Results: With a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 22 patients (28.5%) discontinued treatment: 32% (7/22) due to intolerance and 45% (10/22) due to resistance. Fifty-five percent of the patients reported adverse effects (AEs) with asciminib and eighteen percent grade 3-4. Most frequent AEs were: fatigue (18%), thrombocytopenia (17%), anemia (12%), and arthralgias (12%). None of the patients experienced cardiovascular events or occlusive arterial disease. Further, 26%, 25%, and 9% of patients required dose adjustment, temporary suspension, or definitive discontinuation of treatment, respectively. Toxicities under asciminib seemed lower than with prior TKIs for anemia, cardiovascular events, pleural/pericardial effusion, diarrhea, and edema. Cross-toxicity risk was statistically significant for thrombocytopenia, anemia, neutropenia, fatigue, vomiting, and pancreatitis. (4) Conclusion: Asciminib is a molecule with a good safety profile and with a low rate of AEs. However, despite its new mechanism of action, asciminib presents a risk of cross-toxicity with classical TKIs for some AEs.
Keywords: asciminib; chronic myeloid leukemia; drug intolerance; toxicities.
Conflict of interest statement
L.P.-L.: Novartis; travel grants. M.P.E.: Novartis; advisory board. J.C.H.-B.: Novartis; advisory board. V.G.-G.: Novartis; BMS; INCYTE; Pfizer; travel grants, research funding, advisory board.
Figures

References
-
- Manley P.W., Barys L., Cowan-Jacob S.W. The specificity of asciminib, a potential treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia, as a myristate-pocket binding ABL inhibitor and analysis of its interactions with mutant forms of BCR-ABL1 kinase. Leuk. Res. 2020;98:106458. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106458. - DOI - PubMed

