ONEST (Observers Needed to Evaluate Subjective Tests) Analysis of Stromal Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (sTILs) in Breast Cancer and Its Limitations
- PMID: 36831541
- PMCID: PMC9954449
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15041199
ONEST (Observers Needed to Evaluate Subjective Tests) Analysis of Stromal Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (sTILs) in Breast Cancer and Its Limitations
Abstract
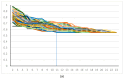
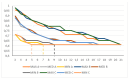
Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) reflect antitumour immunity. Their evaluation of histopathology specimens is influenced by several factors and is subject to issues of reproducibility. ONEST (Observers Needed to Evaluate Subjective Tests) helps in determining the number of observers that would be sufficient for the reliable estimation of inter-observer agreement of TIL categorisation. This has not been explored previously in relation to TILs. ONEST analyses, using an open-source software developed by the first author, were performed on TIL quantification in breast cancers taken from two previous studies. These were one reproducibility study involving 49 breast cancers, 23 in the first circulation and 14 pathologists in the second circulation, and one study involving 100 cases and 9 pathologists. In addition to the estimates of the number of observers required, other factors influencing the results of ONEST were examined. The analyses reveal that between six and nine observers (range 2-11) are most commonly needed to give a robust estimate of reproducibility. In addition, the number and experience of observers, the distribution of values around or away from the extremes, and outliers in the classification also influence the results. Due to the simplicity and the potentially relevant information it may give, we propose ONEST to be a part of new reproducibility analyses.
Keywords: European Working Group for Breast Screening Pathology; ONEST; TILs; breast cancer; international immuno-oncology biomarker working group; observers needed to evaluate subjective tests; reproducibility; sTILs; triple-negative; tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- El Bairi K., Haynes H.R., Blackley E., Fineberg S., Shear J., Turner S., de Freitas J.R., Sur D., Amendola L.C., Gharib M., et al. The tale of TILs in breast cancer: A report from The International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. N.P.J. Breast Cancer. 2021;7:150. doi: 10.1038/s41523-021-00346-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denkert C., von Minckwitz G., Darb-Esfahani S., Lederer B., Heppner B.I., Weber K.E., Budczies J., Huober J., Klauschen F., Furlanetto J., et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:40–50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loi S., Drubay D., Adams S., Pruneri G., Francis P.A., Lacroix-Triki M., Joensuu H., Dieci M.V., Badve S., Demaria S., et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis: A pooled individual patient analysis of early-stage triple-negative breast cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:559–569. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

