Association between Tumor Mutational Burden, Stromal CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, and Clinical Factors in Cervical Cancers Treated with Radiotherapy
- PMID: 36831552
- PMCID: PMC9954714
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15041210
Association between Tumor Mutational Burden, Stromal CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, and Clinical Factors in Cervical Cancers Treated with Radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Tumor mutational burden (TMB) and stromal CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (CD8+TILs) serve important roles in antitumor immune responses to radiotherapy. This study aimed to elucidate the association between TMB, CD8+TILs, and clinical factors in patients with cervical cancer treated with radiotherapy.
Methods: Patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated with definitive radiotherapy, and with available somatic mutation data and immunohistochemical staining data from identical tumor tissues, were enrolled retrospectively. The association between TMB and/or CD8+TIL density and patient characteristics, mutation profiles, and treatment outcome was analyzed.
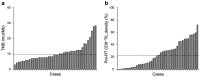
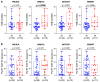
Results: The study analyzed 44 patients (median follow-up period, 61 months). There was no significant correlation between TMB and CD8+TIL density, or between TMB or CD8+TIL density and patient characteristics. TMB-high or CD8+TIL density-low status was associated with worse overall survival and distant metastasis-free survival; the predictive value of these factors became greater when used in combination. TMB-high or CD8+TIL density-high status was associated with ARID1A mutations.
Conclusions: These data indicate independence of TMB and CD8+TIL density and the involvement of ARID1A alterations in antitumor immune responses in patients with cervical cancers treated with radiotherapy, warranting further mechanistic research and prospective validation.
Keywords: ARID1A; CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte; cervical cancer; immune response; radiotherapy; tumor mutational burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders played no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genomic landscape and its correlations with tumor mutational burden, PD-L1 expression, and immune cells infiltration in Chinese lung squamous cell carcinoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Jul 12;12(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0762-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31299995 Free PMC article.
-
High tumor mutational burden predicts worse prognosis for cervical cancer treated with radiotherapy.Jpn J Radiol. 2022 May;40(5):534-541. doi: 10.1007/s11604-021-01230-5. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Jpn J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34860358 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor mutational burden and immune infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma and matched brain metastases.ESMO Open. 2021 Apr;6(2):100057. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100057. Epub 2021 Feb 12. ESMO Open. 2021. PMID: 33588158 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes across Human Tumor Types Reveals a Higher Proportion of Bystander CD8+ T Cells in Non-Melanoma Cancers Compared to Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 12;12(11):3344. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113344. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33198174 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6668-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32131780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The molecular mechanism of actions and clinical utilities of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in gastrointestinal cancers: a comprehensive review and future prospects toward personalized medicine.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 24;14:1298891. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1298891. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autologous Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Mono-Therapy Can Rapidly Shrank Tumor in Asian Patient with Stage III/IV Cervical Cancer: Two Cases Report.Int J Womens Health. 2024 Jan 9;16:31-39. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S446768. eCollection 2024. Int J Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38222312 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of Hematoxylin and eosin staining tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (H&E-TILs) in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2023 Dec 5;23(1):1193. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11684-7. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38053017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pötter R., Tanderup K., Schmid M.P., Jürgenliemk-Schulz I., Haie-Meder C., Fokdal L.U., Sturdza A.E., Hoskin P., Mahant-shetty U., Segedin B., et al. MRI-guided adaptive brachytherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer (EMBRACE-I): A multicentre prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:538–547. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30753-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

