Targeting the Tumor Immune Microenvironment Could Become a Potential Therapeutic Modality for Aggressive Pituitary Adenoma
- PMID: 36831707
- PMCID: PMC9954754
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13020164
Targeting the Tumor Immune Microenvironment Could Become a Potential Therapeutic Modality for Aggressive Pituitary Adenoma
Abstract
Object: This study aimed to explore the relationship between the aggressiveness and immune cell infiltration in pituitary adenoma (PA) and to provide the basis for immuno-targeting therapies.
Methods: One hundred and three patients with PA who underwent surgery at a single institution were retrospectively identified. The infiltration of macrophages and T-lymphocytes was quantitatively assessed.
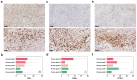
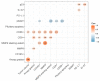
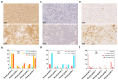
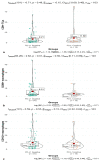
Results: The number of CD68+ macrophages was positively correlated with Knosp (p = 0.003) and MMP-9 expression grades (p = 0.00). The infiltration of CD163+ macrophages differed among Knosp (p = 0.022) and MMP-9 grades (p = 0.04). CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were also positively associated with Knosp (p = 0.002) and MMP-9 grades (p = 0.01). Interestingly, MGMT expression was positively correlated with MMP-9 staining extent (p = 0.000). The quantities of CD8+ TILs (p = 0.016), CD68+ macrophages (p = 0.000), and CD163+ macrophages (p = 0.043) were negatively associated with MGMT expression levels. The number of CD68+ macrophages in the PD-L1 negative group was significantly more than that in the PD-L1 positive group (p = 0.01). The rate of PD-L1 positivity was positively correlated with the Ki-67 index (p = 0.046) and p53 expression (p = 0.029).
Conclusion: Targeted therapy for macrophages and CD8+ TILs could be a helpful treatment in the future for aggressive PA. Anti-PD-L1 therapy may better respond to PAs with higher Ki-67 and p53 expression and more infiltrating CD68+ macrophages. Multiple treatment modalities, especially combined with immunotherapy could become a novel therapeutic strategy for aggressive PA.
Keywords: CD8+ TILs; aggressive pituitary adenoma; combined immunotherapy; immune microenvironment; macrophage; temozolomide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nomikos P., Buchfelder M., Fahlbusch R. The outcome of surgery in 668 patients with acromegaly using current criteria of biochemical ‘cure’. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005;152:379–387. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

