A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors
- PMID: 36831906
- PMCID: PMC9954386
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13020362
A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors
Abstract
Background: Brainstem tumors are rare and extremely heterogeneous and present significant challenges in surgical treatment. Thus, biopsies often set the foundation for the diagnosis of brainstem tumors. Multimodal, image-guided, robot-assisted frameless stereotactic biopsies are increasingly popular in neurosurgery centers. This study aimed to compare the safety, efficacy, and duration of the Remebot robot-assisted (Remebot) frameless brainstem tumor biopsy versus those of frame-based stereotactic biopsy.
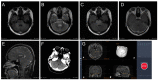
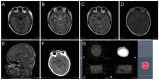
Method: A retrospective analysis of 33 patients with brainstem tumors who underwent stereotactic brainstem biopsies in the department of neurosurgery from January 2016 to January 2021 was conducted. The patients were divided into two groups: the Remebot group (n = 22) and the frame-based group (n = 11). The clinical characteristics, trajectory strategy, duration of procedure, diagnostic yielding, histopathological diagnosis, and postoperative complications were retrospectively analyzed and compared between the groups.
Results: More pediatric patients performed Remebot frameless brainstem tumor biopsy than frame-based biopsy, with a mean age of 17.3 ± 18.7 vs. 32.8 ± 17.1 (p = 0.027). The diagnostic yield had no significant difference in the two groups, with the diagnostic yield of frame-based biopsy and Remebot frameless brain biopsy being 90.9% and 95.5%, respectively. The time of the total process was 124.5 min for the frame-based biopsy and 84.7 min for the Remebot frameless brain biopsy (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences with respect to the occurrence of complication or the duration of the operation between the two groups.
Conclusion: Remebot frameless stereotactic brainstem biopsy is as safe and efficacious as frame-based stereotactic biopsy. However, Remebot frameless biopsy can reduce the total duration of the procedure and has better application in young pediatric patients. Remebot frameless stereotactic biopsies can be a better option towards the safe and efficient treatment of brainstem tumors.
Keywords: Remebot robot; biopsy; brainstem tumor; frameless; stereotactic surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Price M., Ryan K., Edelson J., Neff C., Cioffi G.A., Waite K., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Pediatric Brain Tumor Foundation Childhood and Adolescent Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncol. 2022;24:iii1–iii38. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac161. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu S., Wang H., Wang J., Hu F., Jiang W., Lei T., Shu K. Effect of Robot-Assisted Neuroendoscopic Hematoma Evacuation Combined Intracranial Pressure Monitoring for the Treatment of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2021;12:722924. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.722924. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncol. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

