Microfluidics for COVID-19: From Current Work to Future Perspective
- PMID: 36831930
- PMCID: PMC9953302
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13020163
Microfluidics for COVID-19: From Current Work to Future Perspective
Abstract
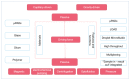
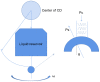
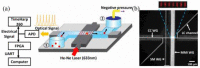
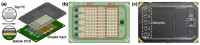
Spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has significantly impacted the public health and economic sectors. It is urgently necessary to develop rapid, convenient, and cost-effective point-of-care testing (POCT) technologies for the early diagnosis and control of the plague's transmission. Developing POCT methods and related devices is critical for achieving point-of-care diagnosis. With the advantages of miniaturization, high throughput, small sample requirements, and low actual consumption, microfluidics is an essential technology for the development of POCT devices. In this review, according to the different driving forces of the fluid, we introduce the common POCT devices based on microfluidic technology on the market, including paper-based microfluidic, centrifugal microfluidic, optical fluid, and digital microfluidic platforms. Furthermore, various microfluidic-based assays for diagnosing COVID-19 are summarized, including immunoassays, such as ELISA, and molecular assays, such as PCR. Finally, the challenges of and future perspectives on microfluidic device design and development are presented. The ultimate goals of this paper are to provide new insights and directions for the development of microfluidic diagnostics while expecting to contribute to the control of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; immunoassays; microfluidic; molecular assays.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



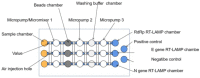
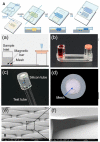
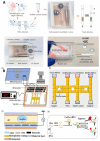

References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard|WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. [(accessed on 31 October 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

