Recent Advances in Microfluidics-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection
- PMID: 36832012
- PMCID: PMC9954504
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13020246
Recent Advances in Microfluidics-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection
Abstract
Using pathogen-infected food that can be unhygienic can result in severe diseases and an increase in mortality rate among humans. This may arise as a serious emergency problem if not appropriately restricted at this point of time. Thus, food science researchers are concerned with precaution, prevention, perception, and immunity to pathogenic bacteria. Expensive, elongated assessment time and the need for skilled personnel are some of the shortcomings of the existing conventional methods. Developing and investigating a rapid, low-cost, handy, miniature, and effective detection technology for pathogens is indispensable. In recent times, there has been a significant scope of interest for microfluidics-based three-electrode potentiostat sensing platforms, which have been extensively used for sustainable food safety exploration because of their progressively high selectivity and sensitivity. Meticulously, scholars have made noteworthy revolutions in signal enrichment tactics, measurable devices, and portable tools, which can be used as an allusion to food safety investigation. Additionally, a device for this purpose must incorporate simplistic working conditions, automation, and miniaturization. In order to meet the critical needs of food safety for on-site detection of pathogens, point-of-care testing (POCT) has to be introduced and integrated with microfluidic technology and electrochemical biosensors. This review critically discusses the recent literature, classification, difficulties, applications, and future directions of microfluidics-based electrochemical sensors for screening and detecting foodborne pathogens.
Keywords: electrochemical; food safety; microfluidics; nanotechnology; pathogens; sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
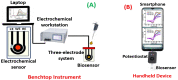

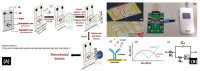

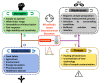
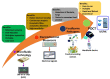
Similar articles
-
Lab-on-a-Chip Electrochemical Biosensors for Foodborne Pathogen Detection: A Review of Common Standards and Recent Progress.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;13(2):215. doi: 10.3390/bios13020215. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advancements in microfluidic chip biosensor detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria: a review.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Apr;414(9):2883-2902. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03872-w. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35064302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Safety Analysis.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;12(12):1088. doi: 10.3390/bios12121088. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A film-based integrated chip for gene amplification and electrochemical detection of pathogens causing foodborne illnesses.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 Oct 16;1027:57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.03.061. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29866270
-
Aptasensor Based on Microfluidic for Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria and Virus Detection: A Review.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024;54(4):872-881. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2022.2099222. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 35831973 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical biosensors in healthcare services: bibliometric analysis and recent developments.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 27;11:e15566. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15566. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37397018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On-Chip Electrochemical Sensing with an Enhanced Detecting Signal Due to Concentration Polarization-Based Analyte Preconcentration.Anal Chem. 2024 Apr 23;96(16):6501-6510. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c01018. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38593185 Free PMC article.
-
Newly Developed Electrochemiluminescence Based on Bipolar Electrochemistry for Multiplex Biosensing Applications: A Consolidated Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;13(6):666. doi: 10.3390/bios13060666. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Electrospun Nanofiber-Based Electrochemical Sensors in Food Safety.Molecules. 2024 Sep 17;29(18):4412. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184412. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A plug-and-play, easy-to-manufacture fluidic accessory to significantly enhance the sensitivity of electrochemical immunoassays.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 19;14(1):14154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64852-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38898088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rivet C., Lee H., Hirsch A., Hamilton S., Lu H. Microfluidics for medical diagnostics and biosensors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011;66:1490–1507. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2010.08.015. - DOI
-
- Pumera M., Merkoçi A., Alegret S. New materials for electrochemical sensing VII. Microfluidic chip platforms. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006;25:219–235. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2005.08.005. - DOI
-
- Puneeth S.B., Kulkarni M.B., Goel S. Microfluidic viscometers for biochemical and biomedical applications: A review. Eng. Res. Express. 2021;3:022003. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/abfd47. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

