Progress in Fluorescence Biosensing and Food Safety towards Point-of-Detection (PoD) System
- PMID: 36832016
- PMCID: PMC9953818
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13020249
Progress in Fluorescence Biosensing and Food Safety towards Point-of-Detection (PoD) System
Abstract
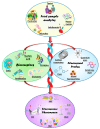
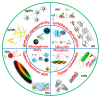
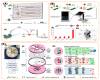
The detection of pathogens in food substances is of crucial concern for public health and for the safety of the natural environment. Nanomaterials, with their high sensitivity and selectivity have an edge over conventional organic dyes in fluorescent-based detection methods. Advances in microfluidic technology in biosensors have taken place to meet the user criteria of sensitive, inexpensive, user-friendly, and quick detection. In this review, we have summarized the use of fluorescence-based nanomaterials and the latest research approaches towards integrated biosensors, including microsystems containing fluorescence-based detection, various model systems with nano materials, DNA probes, and antibodies. Paper-based lateral-flow test strips and microchips as well as the most-used trapping components are also reviewed, and the possibility of their performance in portable devices evaluated. We also present a current market-available portable system which was developed for food screening and highlight the future direction for the development of fluorescence-based systems for on-site detection and stratification of common foodborne pathogens.
Keywords: PoC device; biosensing; fluorescence microscopy; food pathogen; microfluidic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanomaterial-based biosensors for the detection of foodborne bacteria: a review.Analyst. 2023 Nov 20;148(23):5790-5804. doi: 10.1039/d3an01554h. Analyst. 2023. PMID: 37855707 Review.
-
Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Safety Analysis.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;12(12):1088. doi: 10.3390/bios12121088. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Progress in Nanomaterial-Based Fluorescence Assays for the Detection of Food-Borne Pathogens.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 2;24(23):7715. doi: 10.3390/s24237715. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Applications of Nanobiosensors in Pathogen Detection in Water and Food.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;13(10):922. doi: 10.3390/bios13100922. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosensors Coupled with Signal Amplification Technology for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;11(6):190. doi: 10.3390/bios11060190. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207580 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progresses in Optical Biosensors for Interleukin 6 Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 21;13(9):898. doi: 10.3390/bios13090898. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Computer Vision and Spectroscopy Techniques for Non-Destructive Quality Assessment of Citrus Fruits: A Comprehensive Review.Foods. 2025 Jan 24;14(3):386. doi: 10.3390/foods14030386. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39941979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Detection Platform for Determination of Ractopamine in Food.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;14(10):462. doi: 10.3390/bios14100462. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451675 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent-Based Neurotransmitter Sensors: Present and Future Perspectives.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;13(12):1008. doi: 10.3390/bios13121008. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38131768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Europium Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Strip Biosensors Combined with Recombinase Polymerase Amplification for Simultaneous Detection of Five Zoonotic Foodborne Pathogens.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;13(6):652. doi: 10.3390/bios13060652. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shonhiwa A.M., Ntshoe G., Essel V., Thomas J., McCarthy K. A Review of Foodborne Diseases Outbreaks Reported to the Outbreak Response Unit, National Institute for Communicable Diseases, South Africa, 2013–2017. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019;79:73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.11.186. - DOI
-
- Van der Fels-Klerx H.J., Van Asselt E.D., Raley M., Poulsen M., Korsgaard H., Bredsdorff L., Nauta M., D’agostino M., Coles D., Marvin H.J.P. Critical Review of Methods for Risk Ranking of Food-Related Hazards, Based on Risks for Human Health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018;58:178–193. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1141165. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

