Analysis of the Interaction between DNA Aptamers and Cytochrome C on the Surface of Lipid Films and on the MUA Monolayer: A QCM-D Study
- PMID: 36832017
- PMCID: PMC9953847
- DOI: 10.3390/bios13020251
Analysis of the Interaction between DNA Aptamers and Cytochrome C on the Surface of Lipid Films and on the MUA Monolayer: A QCM-D Study
Abstract
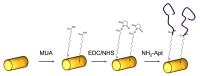
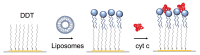
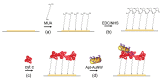
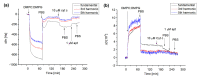
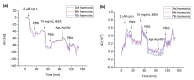
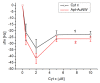
We analyzed the possibility of the detection of cytochrome c (cyt c) being physically adsorbed on lipid films or covalently bounded to 11-mercapto-1-undecanoic acid (MUA) chemisorbed on the gold layer using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). The negatively charged lipid film composed of a mixture of zwitterionic DMPC and negatively charged DMPG phospholipids at a molar ratio of 1:1 allowed the formation of a stable cyt c layer. Addition of DNA aptamers specific to cyt c, however, resulted in removal of cyt c from the surface. The interaction of cyt c with the lipid film and its removal by DNA aptamers were accompanied by changes in viscoelastic properties evaluated using the Kelvin-Voigt model. Cyt c covalently bound to MUA also provided a stable protein layer already at its relatively low concentrations (0.5 μM). A decrease in the resonant frequency following the addition of gold nanowires (AuNWs) modified by DNA aptamers was observed. The interaction of aptamers with cyt c on the surface can be a combination of specific and non-specific interactions due to electrostatic forces between negatively charged DNA aptamers and positively charged cyt c.
Keywords: DNA aptamers; QCM-D; cytochrome c; gold nanowires; lipid films.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probing protein adsorption onto mercaptoundecanoic acid stabilized gold nanoparticles and surfaces by quartz crystal microbalance and zeta-potential measurements.Langmuir. 2007 May 22;23(11):6053-62. doi: 10.1021/la063725a. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Langmuir. 2007. PMID: 17465581
-
Direct electrochemistry and superficial characterization of DNA-cytochrome c-MUA films on chemically modified gold surface.Talanta. 2006 Jan 15;68(3):653-8. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2005.05.009. Epub 2005 Jun 17. Talanta. 2006. PMID: 18970371
-
Structural changes in a polyelectrolyte multilayer assembly investigated by reflection absorption infrared spectroscopy and sum frequency generation spectroscopy.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Feb 12;113(6):1559-68. doi: 10.1021/jp807453w. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19152319
-
Quartz crystal microbalance: a useful tool for studying thin polymer films and complex biomolecular systems at the solution-surface interface.Biomacromolecules. 2003 Sep-Oct;4(5):1099-120. doi: 10.1021/bm020116i. Biomacromolecules. 2003. PMID: 12959572 Review.
-
Label-free, real-time interaction and adsorption analysis 2: quartz crystal microbalance.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;996:313-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-354-1_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23504432 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytochrome c and cancer cell metabolism: A new perspective.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Dec;32(12):102194. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102194. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 39564377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Engineering Planar Model Cell Membranes: Current Techniques, Applications, and Future Perspectives.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;14(18):1489. doi: 10.3390/nano14181489. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Transducer Elements Based on Different Material Configurations for Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 13;14(7):341. doi: 10.3390/bios14070341. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056617 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

