Performance Evaluation of RapiSure (EDGC) COVID-19 S1 RBD IgG/Neutralizing Ab Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
- PMID: 36832131
- PMCID: PMC9955181
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13040643
Performance Evaluation of RapiSure (EDGC) COVID-19 S1 RBD IgG/Neutralizing Ab Test for the Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
Abstract
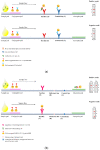
The accurate detection of anti-neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibodies can aid in the understanding of the development of protective immunity against COVID-19. This study evaluated the diagnostic performance of the RapiSure (EDGC) COVID-19 S1 RBD IgG/Neutralizing Ab Test. Using the 90% plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT90) as a reference, 200 serum samples collected from 78 COVID-19-positive and 122 COVID-19-negative patients were divided into 76 PRNT90-positive and 124 PRNT90-negative groups. The ability of the RapiSure test to detect antibodies was compared to that of the STANDARD Q COVID-19 IgM/IgG Plus test and that of PRNT90. The positive, negative, and overall percent agreement between the RapiSure and STANDARD Q test was 95.7%, 89.3%, and 91.5%, respectively, with a Cohen's kappa of 0.82. The RapiSure neutralizing antibody test results revealed a sensitivity of 93.4% and a specificity of 100% compared to the PRNT results, with an overall percent agreement of 97.5% and Cohen's kappa of 0.95. The diagnostic performance of the RapiSure test was in good agreement with the STANDARD Q COVID-19 IgM/IgG Plus test and comparable to that of the PRNT. The RapiSure S1 RBD IgG/Neutralizing Ab Test was found to be convenient and reliable and, thus, can provide valuable information for rapid clinical decisions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19 antibodies; SARS-CoV-2; neutralizing antibodies; rapid chromatographic immunoassay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serological testing for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in clinical practice: A comparative diagnostic accuracy study.Allergy. 2022 Jul;77(7):2090-2103. doi: 10.1111/all.15206. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Allergy. 2022. PMID: 34986501 Free PMC article.
-
Are SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Detectable in Human Milk After Vaccination Against COVID-19?J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022 Apr 30;11(4):126. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piac024. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022. PMID: 35394545 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the Neutralizing Effect and Titer Correlation of Semi-Quantitative Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Immunoassays.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Apr 14;12:822599. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.822599. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35493733 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Humoral Immunity against SARS-CoV-2: Validation of a Plaque-Reduction Neutralization Test and a Multilaboratory Comparison of Conventional and Surrogate Neutralization Assays.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0088621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00886-21. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34787495 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Elecsys Anti-SARS CoV-2 (Roche) and VIDAS Anti-SARS CoV-2 (Biomérieux) for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Spike Protein Antibody Detection.EJIFCC. 2022 Aug 8;33(2):159-165. eCollection 2022 Aug. EJIFCC. 2022. PMID: 36313907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Statement on the Twelfth Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. [(accessed on 29 September 2022)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/12-07-2022-statement-on-the-twelfth-meetin....
-
- Addetia A., Crawford K.H., Dingens A., Zhu H., Roychoudhury P., Huang M.-L., Jerome K.R., Bloom J.D., Greninger A.L. Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with a high attack rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58:e02107–e02120. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02107-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

