Evaluation of Beta-Defensin 1 and Mannose-Binding Lectin 2 Polymorphisms in Children with Dental Caries Compared to Caries-Free Controls: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36832361
- PMCID: PMC9955557
- DOI: 10.3390/children10020232
Evaluation of Beta-Defensin 1 and Mannose-Binding Lectin 2 Polymorphisms in Children with Dental Caries Compared to Caries-Free Controls: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and objective: Some variants in defensin beta 1 (DEFB1) and mannose-binding lectin 2 (MBL2) genes can be associated with oral diseases. Herein, we designed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association of DEFB1 (rs11362, rs1799946, and rs1800972) and MBL2 (rs7096206 and rs1800450) polymorphisms with the susceptibility to dental caries (DC) in children. Materials and methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in the PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane Library databases until 3 December 2022, without any restrictions. The odds ratio (OR), along with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of the effect sizes, are reported. Analyses including a subgroup analysis, a sensitivity analysis, and funnel plot analyses were conducted. Results: A total of 416 records were identified among the databases, and nine articles were entered into the meta-analysis. A significant relationship was found between the T allele of DEFB1 rs11362 polymorphism and DC susceptibility, and the T allele was related to an elevated risk of DC in children (OR = 1.225; 95%CI: 1.022, 1.469; p = 0.028; I2 = 0%). No other polymorphisms were associated with DC. All articles were of moderate quality. Egger's test in homozygous and dominant models demonstrated a significant publication bias for the association of DEFB1 rs1799946 polymorphism with DC risk. Conclusions: The results demonstrated that the T allele of DEFB1 rs11362 polymorphism had an elevated risk for DC in children. However, there were only few studies that evaluated this association.
Keywords: DEFB1 protein; MBL2 protein; dental caries; meta-analysis; polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
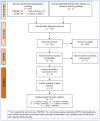


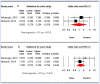


References
-
- Escoffié-Ramirez M., Ávila-Burgos L., Baena-Santillan E.S., Aguilar-Ayala F., Lara-Carrillo E., Minaya-Sánchez M., Mendoza-Rodríguez M., Márquez-Corona M.d.L., Medina-Solís C.E. Factors associated with dental pain in Mexican schoolchildren aged 6 to 12 years. BioMed Res. Int. 2017;2017:7431301. doi: 10.1155/2017/7431301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

